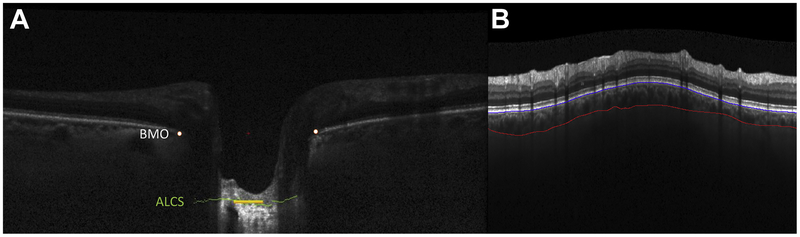
Figure 1.
A Measurement of the anterior lamina cribrosa surface depth (ALCSD). An optical coherence tomography B scan image of a glaucomatous eye after automated segmentation by the San Diego Automated Layer Segmentation Algorithm (SALSA) software. The Bruch’s membrane opening (BMO) is identified (white dots) and a 61 point interval in the middle of the BMO is marked (middle red cross). The detectable anterior lamina cribrosa surface (ALCS) is segmented (green line). The individual ALCSD for the B scan is represented as the median depth of the 61 point interval of lamina points centered from the BMO plane, measured from the BMO plane (yellow line). B. Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography image with SALSA segmentation of the choroid, seen between the Bruch membrane (blue line) and the choroidal–scleral interface (red line).