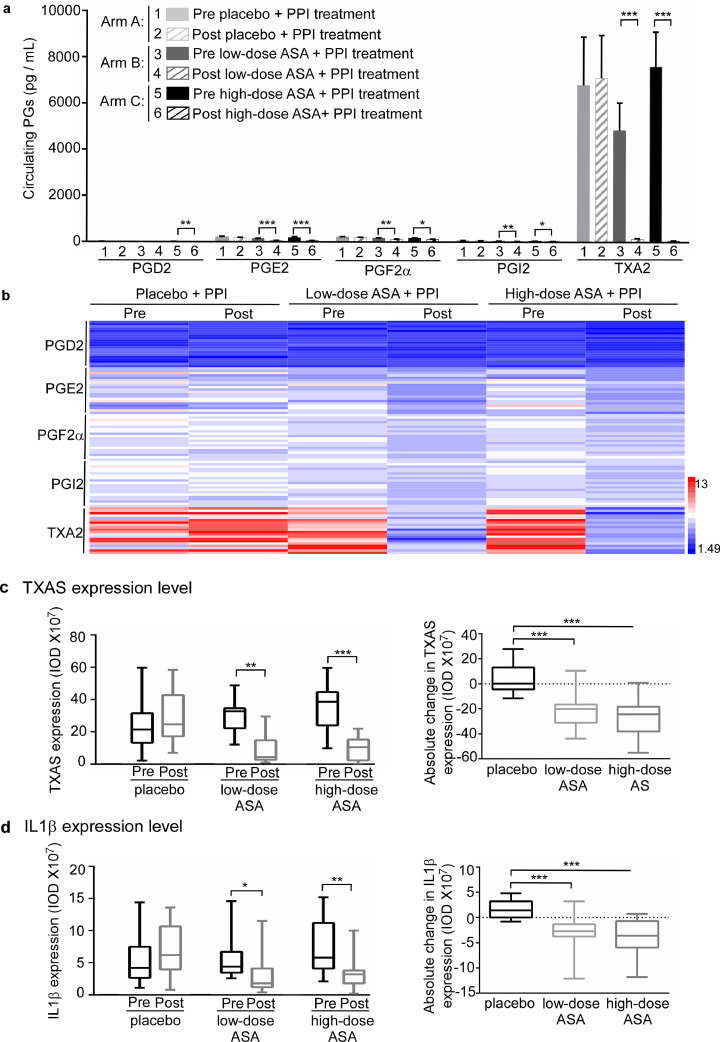
Fig. 4.
Effects of ASA on circulating PG levels and the expression of TBXAS and IL1β in a human clinical trial. a, effects of regular ASA use on circulating PG biosynthesis in pre- and post-treated BE patients were assessed by using an enzyme immunoassay kit: 1 = pre placebo + PPI treatment; 2 = post placebo + PPI treatment; 3 = pre low-dose (81 mg) + PPI treatment; 4 = post low-dose (81 mg) + PPI treatment; 5 = pre high-dose (325 mg) + PPI treatment; 6 = post high-dose (325 mg) + PPI treatment. The summary data are presented as mean values ± S.E. The asterisks indicate a significant difference compared to the pre-treated group. Significant differences were determined by Wilcoxon signed rank test. b, the heat map across all the samples showed the PG levels (log2 scale). c, d, ASA decreases the expression of TBXAS and IL1β in the biopsy specimens from BE patients. An immunohistochemistry assay was conducted to compare expression levels of TBXAS (c) and IL1β (d) in pre-treated and post-treated biopsy specimens from BE patients. Density scores were obtained from each sample and statistical significance was determined by Wilcoxon signed rank test and Wilcoxon rank sum test. Data are presented as mean values ± S.E. from triplicate experiments. The asterisks indicate a significant difference compared to the pre-treated group (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 and ***, p < 0.001, a, Wilcoxon signed rank test; c and d, Wilcoxon signed rank test and Wilcoxon rank sum test).