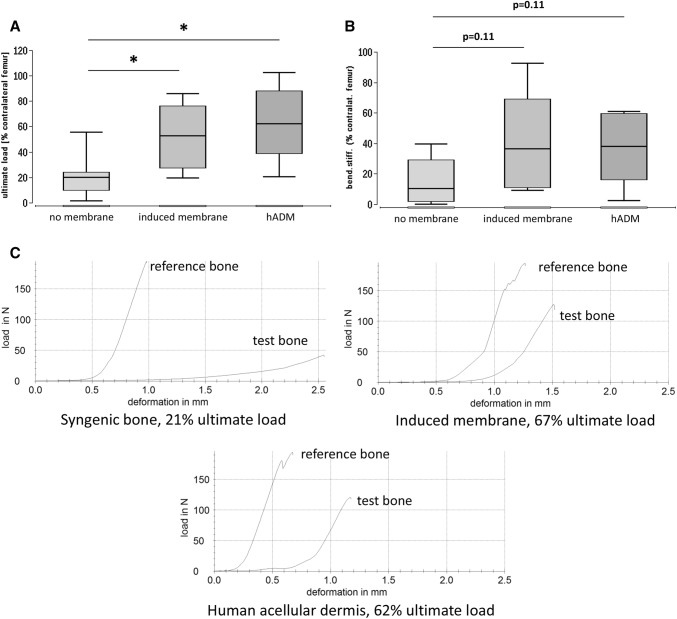
Fig. 4.
Ultimate load (a) and bending stiffness (b) of the defect zone treated with syngenic spongiosa, induced membrane filled with syngenic spongiosa (Masquelet technique) or human acellular dermis (hADM) filled with syngenic spongiosa. Biomechanical properties of the defect zone were measured by means of three-point bending test eight weeks after transplantation. Representative force/deformation curves of femora obtained from animals that received either solely syngenic spongiosa, induced membrane and syngenic spongiosa or human acellular dermis and spongiosa are presented in (c). The callus was not bridged in the control group. The force/deformation curve of the respective healthy contralateral femur is shown for comparison in each example. Peak of the curves indicate the ultimate load of the bone samples. *p < 0.05