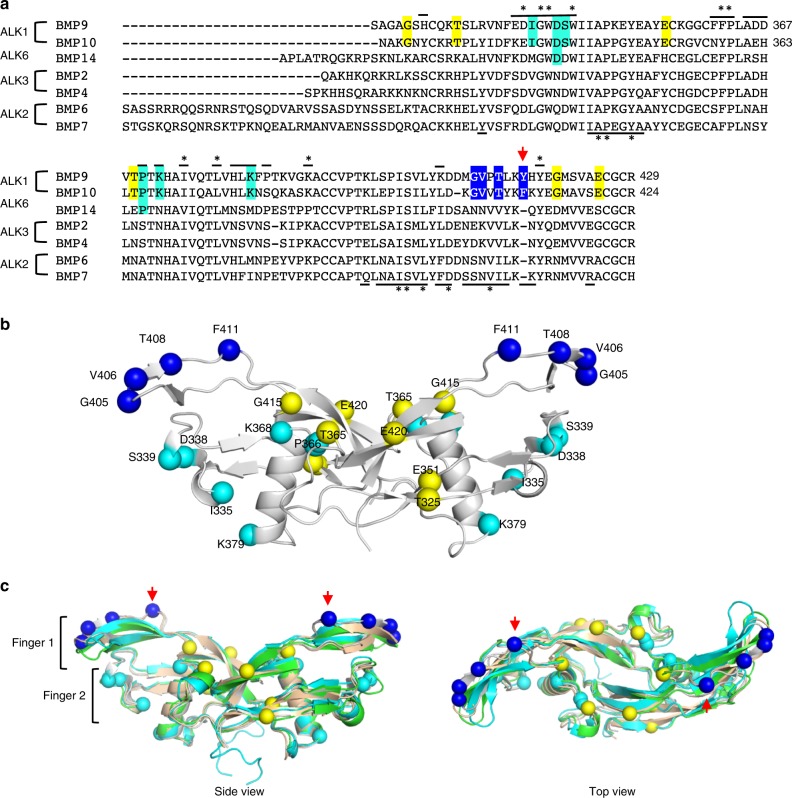
Fig. 3. Specificity determinants in the BMP9 and BMP10 subfamily.
a Sequence alignment of representative ALK-binding BMPs. GF-domain sequences of ALK1-binding BMP9 and BMP10, ALK6-binding BMP14, ALK3-binding BMP2 and BMP4, as well as ALK2-binding BMP6 and BMP7 are aligned. Lines over and below the sequences highlight the residues at the type I and type II receptor-binding surface based on BMP10:ALK1 and BMP9:ALK1:ActRIIb structures, respectively. Asterisk (*) marks the residues that are conserved among at least 6 out of 7 aligned BMPs. Residues preferentially conserved between BMP9 and BMP10 are highlighted, in cyan for those at the type I site (conserved region 1), in blue for those at the type II site (conserved region 2) and in yellow for those outside receptor binding surface (conserved region 3). BMP10 D338 and P366 are also highlighted in cyan because they make conserved interactions with ALK1 in the crystal structure (Fig. 4). b Residues from conserved regions 1–3 plotted on BMP10 structure and labelled with full length proBMP10 residue numbers. Fifteen residues from conserved regions 1–3 are shown in spheres, coloured accordingly. The first Gly from conserved region 3 is not modelled in the crystal structure, and hence not plotted. c An overlay of BMP10 (grey) onto the structures of BMP9 (gold, from 4FAO)9, BMP2 (green, from 2GOO)31 and BMP7 (cyan, from 1M4U)61 is shown from the side view (left) and the top view (right). The red arrows indicate the unique insertion in BMP9 and BMP10.