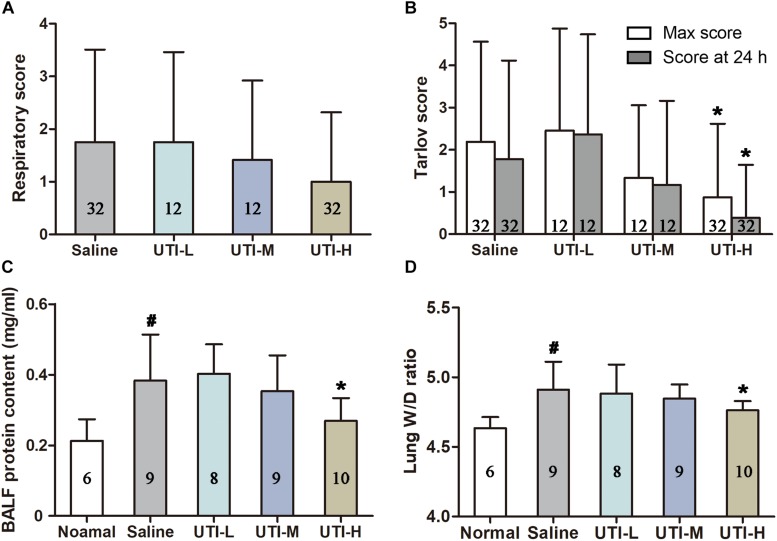
FIGURE 3.
Protective effects of UTI against lung injuries and neurological disorders. Respiratory function was monitored and scored for 2 h following simulated diving. The maximum observed respiratory scores are shown in panel (A). Motor function was evaluated using Tarlov score for 24 h, and UTI-H significantly lowered both the maximal observed scores and scores assessed at 24 h after surfacing (B). The high dose of UTI reduced the elevated BALF protein content and lung W/D ratio (C,D). #P < 0.01 vs. Normal controls, * P < 0.05 vs. Saline group.