Figure 3.
Direct Induction of the Innate Immune Molecule hIFNβ as Output Response in α-HBs SNR Cells
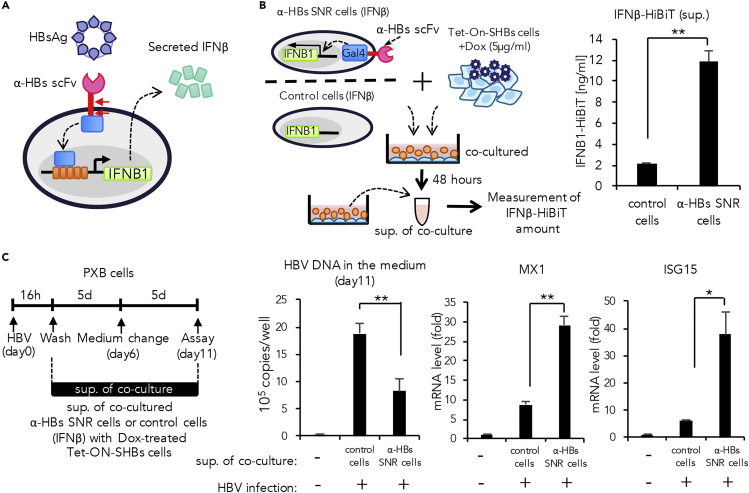
(A) α-HBs SNR cell design for induction of interferon-beta (IFNβ).
(B) Experimental design for induction of IFNβ in α-HBs SNR cells and quantification of induced IFNβ. α-HBs SNR cells were induced with HiBiT-tagged IFNβ by co-culture with Tet-ON-SHBs cells in presence of 5μg/mL doxycycline (Dox). After 48 h, IFNβ-HiBiT in the cell supernatant was quantified. Control cells indicate Jurkat T cells harboring only IFNβ-HiBiT gene without α-HBs SNR. The data shown represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments. **p: <0.01.
(C) Effect of IFNβ derived from the supernatant of α-HBs SNR cells stimulated by HBsAg from Dox-treated Tet-ON-SHBs cells. Primary human hepatocytes (PXB cells) were infected with HBV for 16 h and then were cultured in the presence or absence of supernatant containing α-HBs-SNR-cell-derived IFNβ (30%v/v). HBV DNA in the medium was extracted from these cell supernatants 11 days after infection and quantified using real-time PCR analysis. The expression of representative IFNβ-stimulated genes; MX1 and ISG15, were quantified using qPCR and normalized against the expression of β-actin in PXB cells. Control indicates the cell supernatant of Jurkat T cells harboring only IFNβ-HiBiT gene without α-HBs SNR, co-cultured with Dox-treated Tet-ON-SHBs cells. The data shown represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p: <0.05, **p: < 0.01.