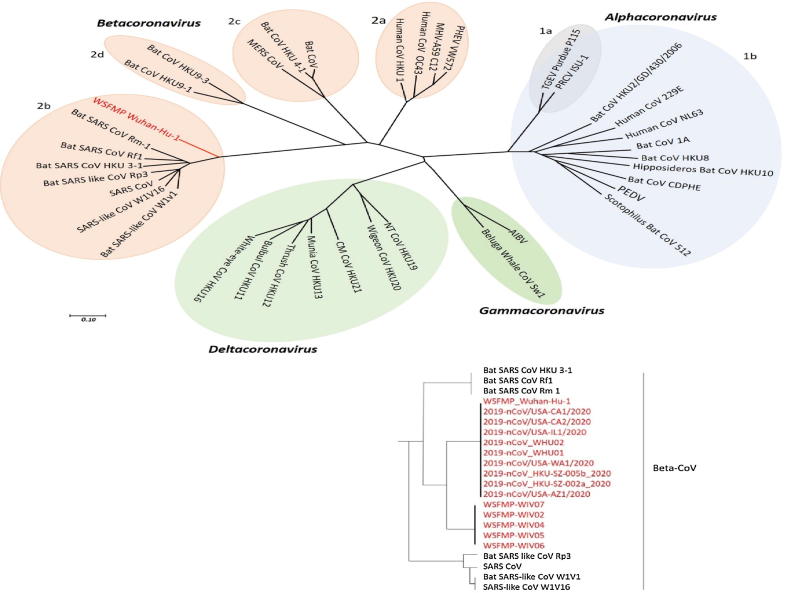
Fig. 5.
Phylogenetic tree of coronaviruses (content in red is the latest addition of newly emerged SARS-CoV-2 and WSFMP Wuhan-Hu-1 is used as a reference in the tree); The phylogenetic tree showing the relationship of Wuhan-Hu-1 (denoted as red) to selected coronavirus is based on nucleotide sequences of the complete genome. The viruses are grouped into four genera (prototype shown): Alphacoronavirus (sky blue), Betacoronavirus (pink), Gammacoronavirus (green) and Deltacoronavirus (light blue). Subgroup clusters are labeled as 1a and 1b for the Alphacoronavirus and 2a, 2b, 2c, and 2d for the Betacoronavirus. This tree is based on the published trees of Coronavirinae [3], [41] and reconstructed with sequences of the complete RNA- dependent RNA polymerase- coding region of the representative novel coronaviruses (maximum likelihood method using MEGA 7.2 software). severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS- CoV); SARS- related coronavirus (SARSr- CoV); the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS- CoV); porcine enteric diarrhea virus (PEDV); Wuhan seafood market pneumonia (Wuhan-Hu-1). Bat CoV RaTG13 Showed high sequence identity to SARS-CoV-2 [42]. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)