Figure 1.
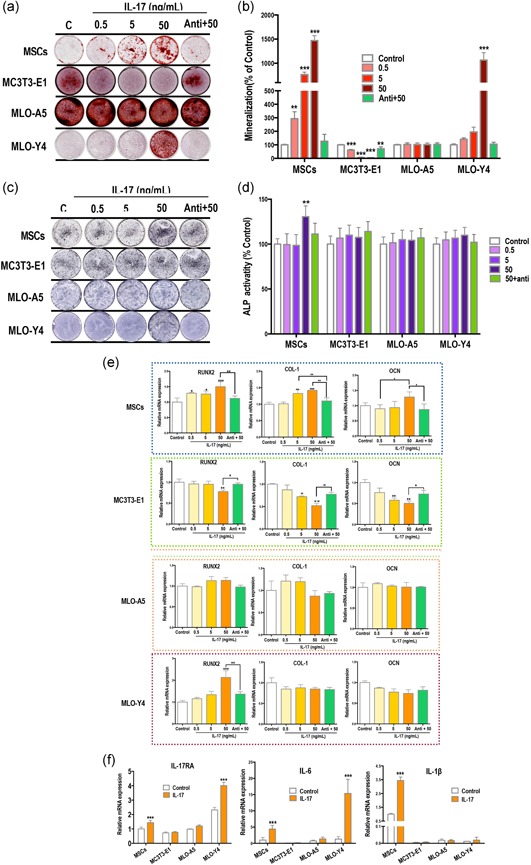
IL‐17 enhances the osteogenic differentiation of mMSCs but not MC3T3‐E1. (a,b) Increased mineralized nodule formation (red) in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and MLO‐Y4 osteocytes after treatment with 0.5–50 ng/ml IL‐17 in osteogenic induction medium for 14 days. Mineralization of MC3T3‐E1 cells was inhibited, and there was no change in mineralization levels in MLO‐A5 cells. (c,d) Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) expression (purple) of MSCs was enhanced by IL‐17 (7 days). (e,f) mRNA expression of factors after IL‐17 treatment for 24 hr. Treatment with IL‐17 increased runt‐related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), collagen‐1 (COL‐1) and osteocalcin (OCN) in MSCs, and only RUNX2 in MLO‐Y4 cells. All three factors were decreased in MC3T3‐E1 cells and no significant changes were measured in MLO‐A5 cells. (f) IL‐17 receptor A (RA) and IL‐6 were upregulated in MSCs and MLO‐Y4 cells, and IL‐β was significantly upregulated in MSCs. IL, interleukin; mMSC, mouse MSCs; mRNA, messenger RNA
