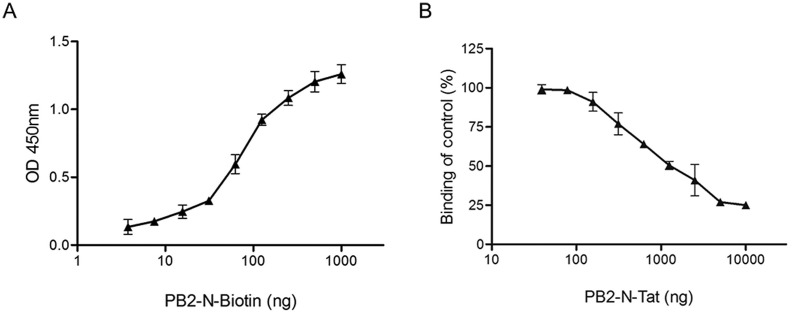
Fig. 2.
Detection of PB1 protein and PB2-N peptide binding by ELISA. (A) The binding curve of PB2-N-Biotin peptide to His-PB1 protein was plotted, in which increasing amounts of PB2-N-Biotin (2-fold diluted from 1 μg/well) were added to wells coated with 200 ng/well of His-PB1. (B) The competitive binding curve of ELISA was shown, in which the peptide PB2-N-Tat was used as a positive control. Increasing concentrations of PB2-N-Tat (2-fold diluted from 10 μg/well) were incubated with 100 ng/well of PB2-N-Biotin probe and added together to the wells coated with 200 ng/well of His-PB1. For both assays, binding intensities were measured with the absorbance at 450 nm. The experiments were conducted in triplicate and repeated twice for confirmation. Data are shown as the mean value ± SD.