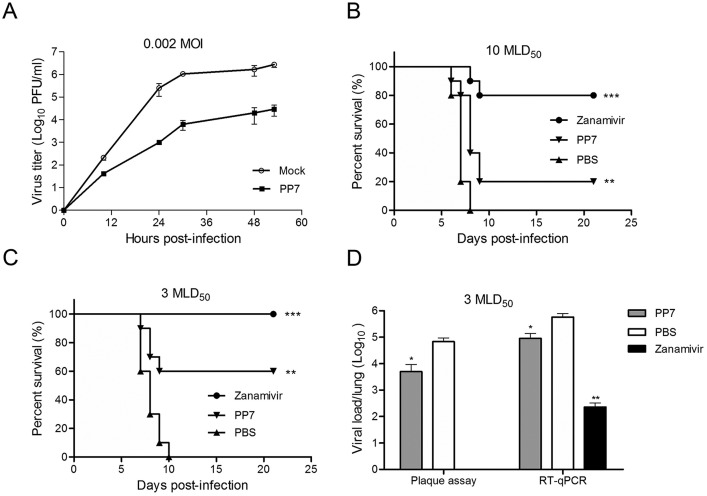
Fig. 4.
Antiviral activities of PP7. (A) In vitro antiviral activity of compound PP7 was evaluated by a multi-cycle virus growth assay. Viral titers in the supernatants, in the presence or absence of 40 μM PP7, were determined by plaque assay at the indicated time-points. Data are represented as mean ± SD of two independent experiments. (B) In vivo antiviral efficacy of PP7 was measured in a lethal mouse model. Mice (10 per group) infected with 10 MLD50 of mouse-adapted A(H1N1)pdm09 virus were treated with 20 μl of 1 mg/ml PP7, 1 mg/ml zanamivir, or PBS by intranasal administration. Treatments started at 4 h after virus challenge and continued for 4 doses in 2 days (2 doses/day). Conditions of the mice were monitored for 21 days or till death. (C) The same treatment regimen was applied to mouse groups that were challenge with 3 MLD50 of mouse-adapted A(H1N1)pdm09 virus. Shown are the survival curves. For both (B) and (C), differences between groups were compared and analyzed using Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. *** indicates p < 0.001 and ** indicates p < 0.01 as compared to PBS-treated group. (D) Mice were infected with 3 MLD50 of mouse-adapted A(H1N1)pdm09 virus. Three mice from each group were euthanized at day 4 post-infection and lungs were collected for detection of viral loads by plaque assay and RT-qPCR. The results are presented as the mean values + SD. Differences between groups were compared using the unpaired t-test. * indicates p < 0.05 and ** indicates p < 0.01 as compared to PBS-treated group. Infectious virus was undetectable in the zanamivir-treated mouse lungs using plaque assay.