Figure 1: Fibromuscular Dysplasia in Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection.
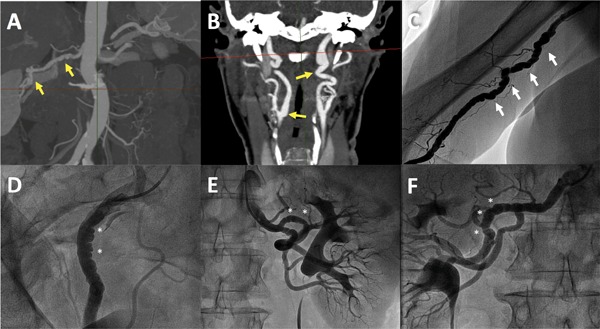
A and B: Angio-CT showing signs of multifocal fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) with zones of stenosis alternating with dilatation in right renal artery (A) and both bilateral carotid arteries (B) in a 67-year-old woman with spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD). C: Angiogram of the brachial artery confirming the typical string-of-beads appearance of multifocal FMD in a 70-year-old patient with SCAD. D-F: Selective angiograms with signs of multifocal FMD in right external iliac artery (D) and both left (E) and right (F) renal arteries in a 60-year-old woman with previous SCAD.
