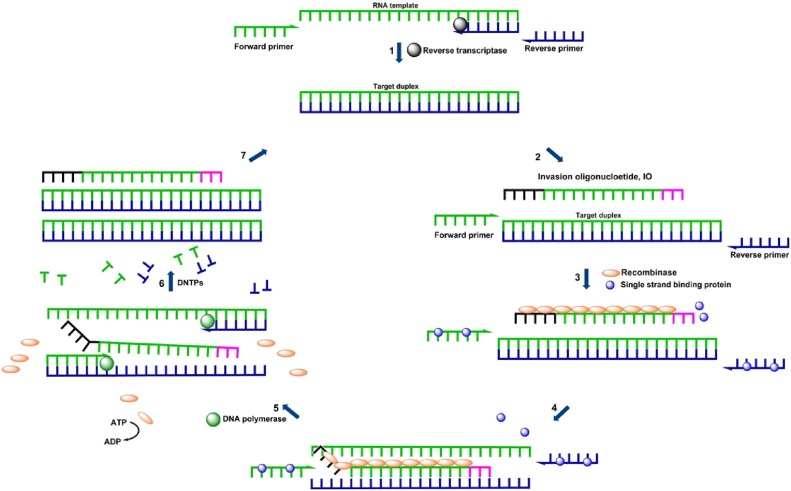
Fig. 1.
Rhinovirus amplification by reverse-transcription strand invasion–based amplification (RT-SIBA). 1) Rhinovirus RNA is reverse transcribed to cDNA by the reverse transcriptase enzyme 2) SIBA amplification requires an invasion oligonucleotide (IO) and two target-specific primers. 3) Single strand binding protein, Gp32 binds to oligonucleotides in order to reduce the formation of secondary structures. The recombinase protein, UvsX, coats the IO displacing the bound Gp32. 4) The recombinase-IO complex invades and separates the target duplex. 5) This allows target-specific primers to bind and extend the target via the action of a DNA polymerase. 6) This leads to the synthesis of two copies of the target duplex. 7) The continuous recombinase-mediated target duplex separation and DNA polymerase extension process leads to an exponential amplification under isothermal conditions.