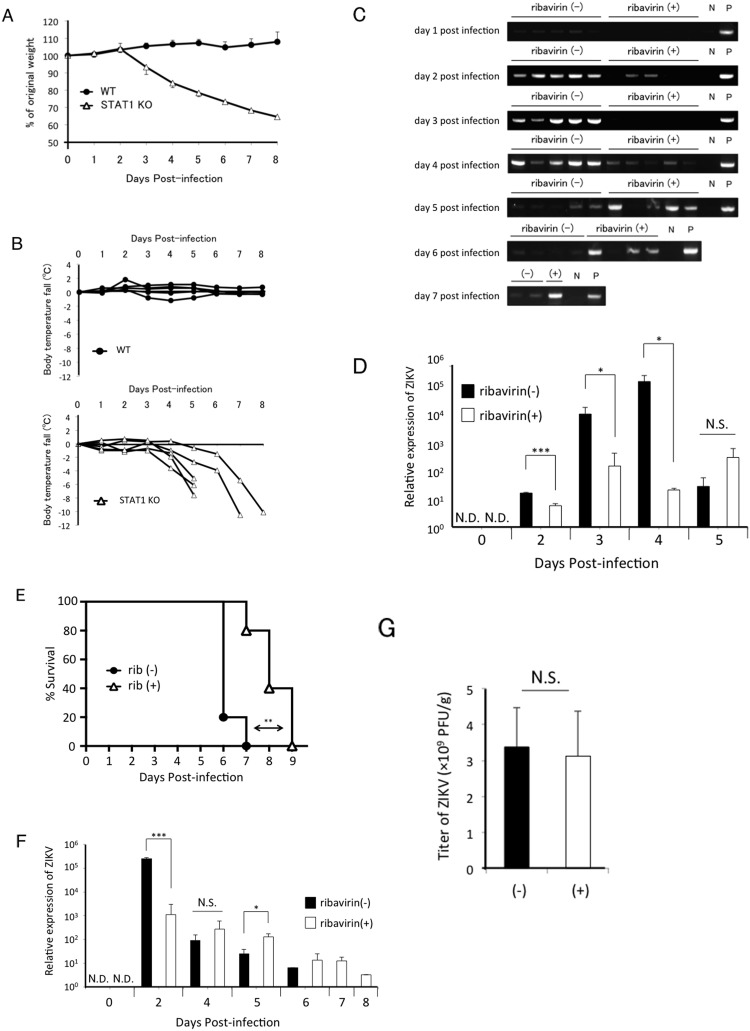
Fig. 6.
Analysis of viremia and survival of ZIKV-infected STAT1-deficient mice. STAT1-deficient mice were subcutaneously infected with 1.0 × 104 PFU of ZIKV per mouse. (A) The average of body weight (n = 6) and (B) individual rectal temperature curves (n = 5) were shown. (C) 15 mg of ribavirin (ribavirin +) (n = 5) or PBS (ribavirin −) (n = 5) was administered intraperitoneally for 3 consecutive days post-infection. Blood samples were collected daily from infected mice, and mRNA was extracted. Expression of ZIKV RNA was analysed by RT-PCR. N: no template control. P: positive control using viral diluent as a template. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (D) The quantitative expression levels of Zika virus. Blood serum samples in (C) were measured by real-time RT-PCR assay (n = 3 or 4 per group). The bar graph represents the mean and standard deviation values. N.S., not significant; ***, P < 0.001. *, P < 0.05. (E) 10 mg of ribavirin (rib +) (n = 5) or PBS (rib −) (n = 5) was administered intraperitoneally everyday. Survival rates were monitored. **, P < 0.01. (F) The quantitative expression levels of Zika virus. Blood serum samples in (E) were measured by real-time RT-PCR assay as shown (D). (G) The titration of brains on day 5 post infection in (C) was performed by plaque assay. The bar graph represents the mean ± S.D. N.S., not significant.