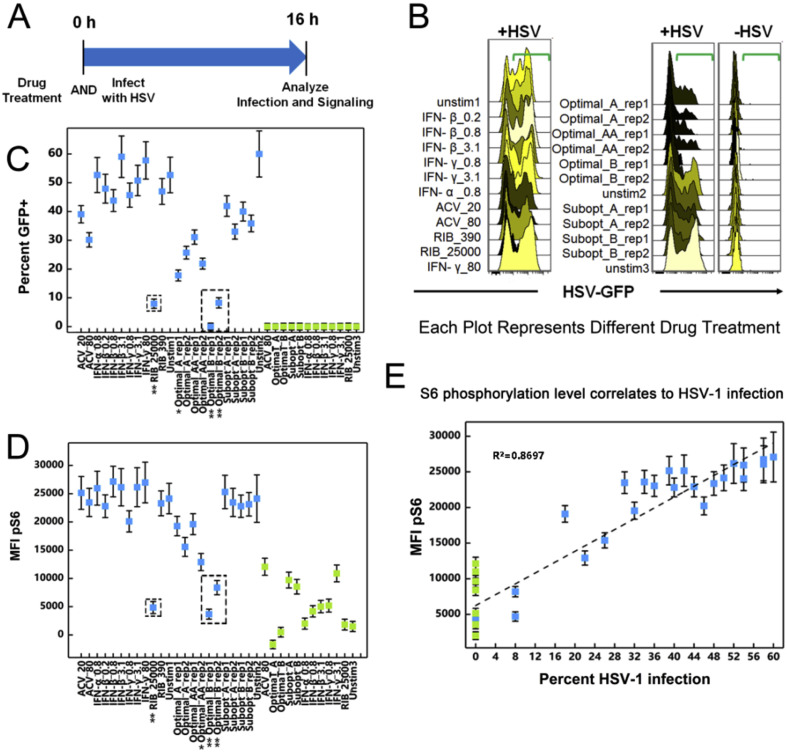
Fig. 5.
Signaling In Simultaneous Infection and Treatment. A. Host cells stimulated with drug combinations and HSV-1 infection simultaneously for 16 h. B. Both drug combinations Optimal_A and Optimal_B profoundly reduced HSV-1 infection compared to unstimulated controls in the co-treated model. Data points are average of data from three experimental ± standard deviation. Flow cytometry histograms are color-coded as in a heatmap with black being unchanged and shades of yellow denoting increases. C. Drug treatments versus percent HSV-1 infection. Data points are average of data from three experimental ± standard deviation. D. Drug treatments versus pS6 level showed similar patterns as viral infection. E. HSV-1 infection levels and S6 phosphorylation levels followed a log-linear correlation. Data points are average of data from three experimental ± standard deviation. As a reminder: high dose IFNs and ACV (Optimal_A and Optimal_AA), high dose RIB and ACV (Optimal_B), low dose IFNs and ACV (Subopt_A), and low dose IFNs and RIB (Subopt_B). All experimental data shown is representative data from three independent experiments. For Parts C, D and E, data plotted is mean ± standard deviation. In Part E, the correlation coefficient, R2, is displayed.