Fig. 2.
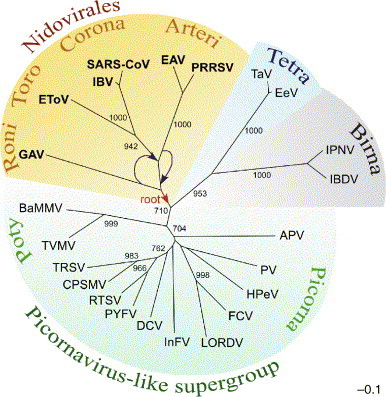
RdRp-based RNA virus tree that includes nidoviruses. The most conserved part of RdRps from representative viruses in the Picornaviridae, Dicistroviridae, Sequiviridae, Comoviridae, Caliciviridae, Potyviridae, Coronaviridae, Roniviridae, Arteriviridae, Birnaviridae, Tetraviridae and unclassified insect viruses was aligned. An unrooted neighbour-joining tree was inferred using the ClustalX1.81 software. For details of the analysis, see Gorbalenya et al. (2002). All bifurcations with support in >700 out of 1000 bootstraps are indicated. Different groups of viruses are highlighted with different colours. The tree was modified from (Gorbalenya et al., 2002, Snijder et al., 2005b, Spaan et al., 2005b). Virus families/groups and abbreviations of viruses included in the analysis are as follows: Coronaviridae: avian infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), severe acute respiratory syndrome virus (SARS-CoV) and Equine torovirus (EToV); Arteriviridae, Equine arteritis virus (EAV) and Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus strain VR-2332 (PRRSV); Roniviridae: Gill-associated virus (GAV); Picornaviridae, human poliovirus type 3 Leon strain (PV) and parechovirus 1 (HPeV); Iflavirus, infectious flacherie virus (InFV); unclassified insect viruses, Acyrthosiphon pisum virus (APV); Dicistroviridae, Drosophila C virus (DCV); Sequiviridae, Rice tungro spherical virus (RTSV) and Parsnip yellow fleck virus (PYFV); Comoviridae, Cowpea severe mosaic virus (CPSMV) and Tobacco ringspot virus (TRSV); Caliciviridae, Feline calicivirus F9 (FCV) and Lordsdale virus (LORDV); Potyviridae, Tobacco vein mottling virus (TVMV) and Barley mild mosaic virus (BaMMV); Tetraviridae, Thosea asigna virus (TaV) and Euprosterna elaeasa virus (EeV); Birnaviridae, infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) and infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV). A plausible direction to the root of the nidovirus domain is indicated (red arrow). As discussed in the text, arteriviruses rather than roniviruses might have been the first to branch off from the nidovirus trunk. This revised topology of the two lineages is also indicated (blue arrows).
