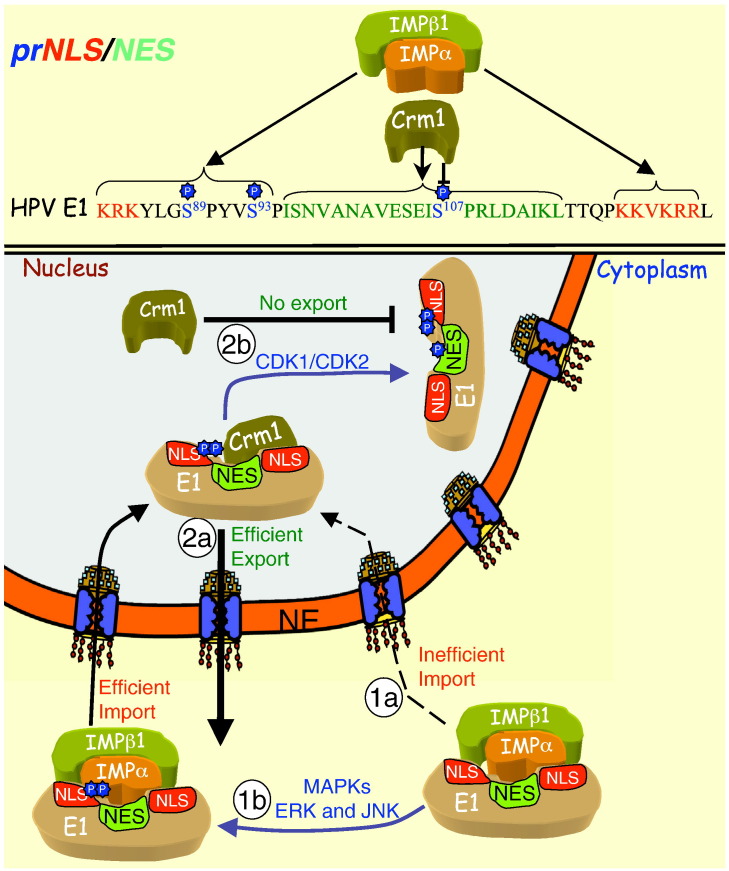
Fig. 5.
Cell cycle-dependent regulation of nuclear localisation for HPV E1 by cellular kinases. The prNLS of HPV E1 is shown (top), with the regulatory phosphorylation sites (blue), NLS (red) and NES (green), highlighted, as well as the binding partners that recognise them according to phosphorylation state (“P” indicates phosphorylation). The E1 NLS mediates IMPα/β1-mediated nuclear import inefficiently (black dotted arrow) (1a) but upon phosphorylation of S89 and S93 by ERK (and/or JNK for S89), IMPα/β1 is able to bind the NLS more strongly to facilitate efficient nuclear import (1b). Once in the nucleus E1 is quickly exported back to the cytoplasm, through Crm1 (2a). Nuclear export is prevented by the nuclear kinases Cdk1/Cdk2 (2b), present during S and G2 phases of cell cycle, which phosphorylate S107 to prevent Crm1 binding to the NES, leading to strong nuclear accumulation/nuclear retention.