Fig. 2.
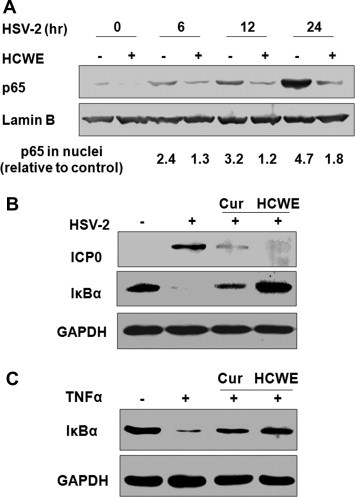
HSV-2 infection induces NF-κB activation and HCWE treatment blocks NF-κB activation. HeLa 229 cells were infected with HSV-2 (MOI = 5) in the presence or absence of 450 μg/ml HCWE for 6, 12 and 24 h. NF-κB/p65 nuclear translocation was determined by protein fractionation followed by immunoblotting with anti-p65 antibody. HSV-2 infection induced persistent NF-κB/p65 protein nuclear translocation, while treatment with HCWE blocked NF-κB/p65 activation induced by HSV-2 infection (A). The numbers represent relative intensity of a p65 protein band to Lamin B, a loading control, in each sample compared to untreated and uninfected control. In separate experiments, curcumin, a known inhibitor of NF-κB activation and HSV-2 immediate early gene expression, was included as a control. Treatment with curcumin (Cur) at 10 μM or HCWE at 450 g/ml significantly blocked HSV-2 ICP0 expression as detected at 24 h PI (B) as well as infection and TNFα induced IκBα degradation (B and C).
