Fig. 3.
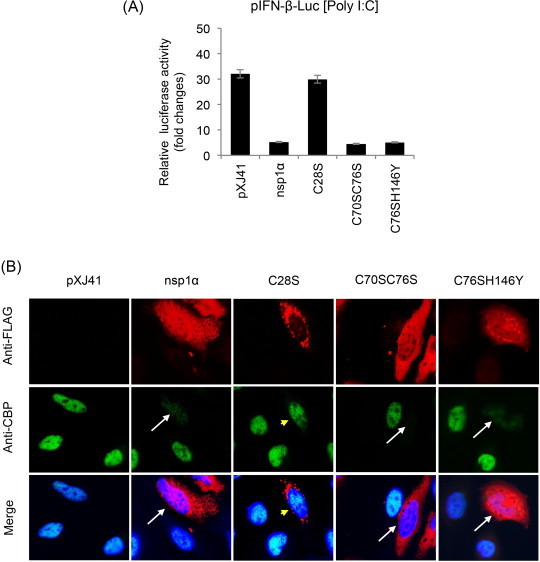
Functional motifs in PRRSV nsp1α for IFN suppression. (A) Mutants of nsp1α were constructed to substitute C28, C70, C76, and H146 to knockout ZF1, PLPα, and ZF2, respectively. C28S, C70SC76S, and C76SH146Y mutants represent three distinct groups; ZF1-destruction mutants, ZF2-destruction mutants, and PLP1α-destruction mutants, respectively. These mutants were expressed in HeLa cells by co-transfection of 500 ng of pIFN-β-Luc along with 50 ng of pTK-RL as an internal control. At 24 h post-transfection, cells were stimulated by 1 μg/ml of poly(I:C) for 12 h followed by determination of reporter expression using the dual luciferase assay system (Promega). Relative luciferase activities were calculated by normalizing the firefly luciferase to renilla luciferase according to the manufacturer's protocol. The data represent the means of three independent experiments, each experiment in triplicate. (B) Degradation of CBP by PRRSV-nsp1α in HeLa cells. Individual mutants of PRRSV-nsp1α were expressed and co-stained with rabbit anti-FLAG Ab and mouse anti-CBP Ab for 2 h, followed by staining with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated (green) and Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated (red) secondary antibodies, respectively, along with DAPI for nucleus staining (blue). Arrows indicate cells where CBP is degraded, and arrowheads (yellow) indicate no CBP degradation.
