Fig. 2.
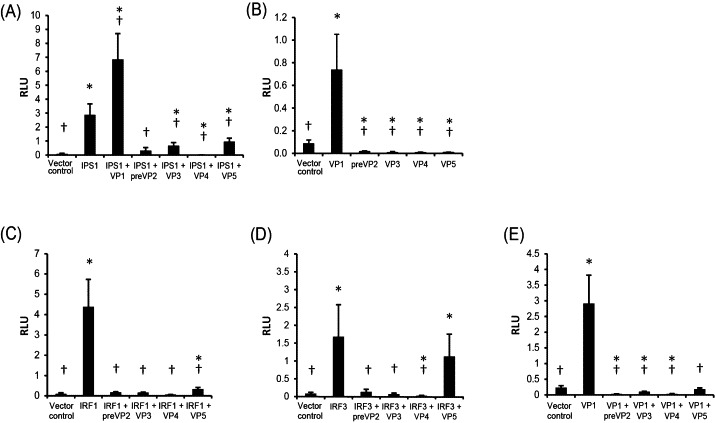
Effect of IPNV proteins on activation of the Atlantic salmon IFNa1 promoter. In all experiments TO-cells were co-transfected with four expression constructs; a plasmid containing the IFNa1 promoter fused to a luciferase gene, a plasmid containing the Renilla luciferase gene as a transfection control, a plasmid containing an IPNV gene (VP1-VP5), and a control plasmid or a plasmid containing a gene encoding a signaling protein in the IFNa1 induction pathway. Samples were harvested 48 h after transfection and analyzed for promoter activation by measuring luciferase activity. Results are presented as mean relative light units (RLU) ± SD (N = 3). (A) Effect of IPNV proteins on IPS-1 mediated activation of the promoter. Significant differences (p < 0.05) from vector control and IPS-1 indicated by * and †, respectively. (B) Effect of the individual IPNV proteins on promoter activation. Significant difference (p < 0.05) from vector control and IPS-1 indicated by * and †, respectively. (C) Effect of IPNV proteins on IRF1 mediated activation of the promoter. Significant differences (p < 0.05) from vector control and IRF-1 indicated by * and †, respectively. (D) Effect of IPNV proteins on IRF3 mediated activation of the promoter. Significant differences (p < 0.05) from vector control and IRF-3 indicated by * and †, respectively. (E) Effect of IPNV proteins on VP1 mediated activation of the promoter. Significant differences (p < 0.05) from vector control and VP1 indicated by * and †, respectively.
