Fig. 5.
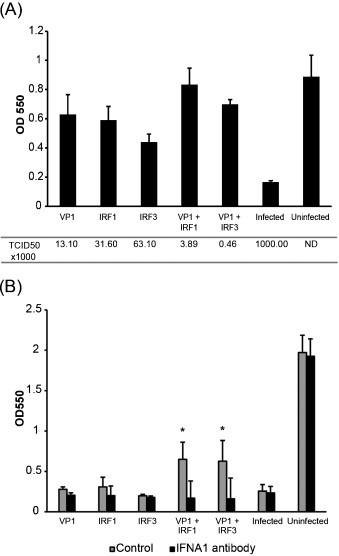
Antiviral activity of VP1, IRF1 and IRF3 against IPNV. (A) TO-cells were transfected with expression constructs for VP1, IRF1, IRF3 alone or VP1 in combination with IRF1 or IRF3, or empty vector for control samples. Three days after transfection, supernatants from the transfected cells were harvested and kept for use in the IFN neutralization assay shown in (B) while the cells were infected with IPNV (MOI 0.1). When full CPE was observed after 4 days, the supernatants were harvested for viral titration, and the surviving cell layer was stained with crystal violet. Cell survival was determined by measuring the absorbance at 550 nm. Viral titers in medium supernatants from the different treatment groups were determined by the TCID50 method. All groups are different from infected control (p < 0.05). (B) Measurement of IFN activity in cell supernatants described in (A) in the presence or absence of neutralizing antibody against IFNa1. TO-cells were treated with supernatants for 24 h and then infected with IPNV as described for (A). At full CPE, cell survival was determined by staining cells with crystal violet and measuring absorbance at 550 nm. Asterisks denote significant differences from infected vector control (p < 0.05).
