Fig. 5.
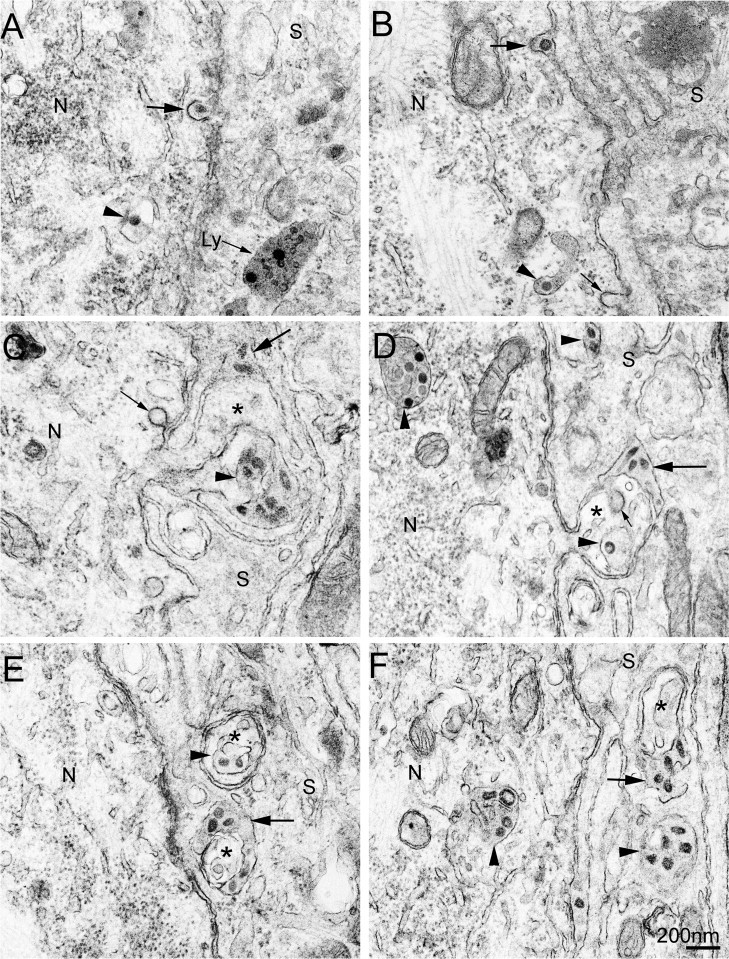
HEV transfer between DRG neurons and their SCs. Scale bar: 200 nm. Neurons (N) and SCs (S) are marked in all images. Arrowheads indicate virus-containing vesicular structures in the cytoplasm of neurons or SCs. Large arrows indicate extracellular virus particles between the neuronal cell bodies and their SCs. Small arrows indicate empty coated vesicles or invaginations. Top row panels show coated vesicle-mediated HEV transfer. Panel A shows a coated vesicle containing a single virion fusing with the plasma membrane of an infected neuron. A lysosome-like structure (arrow labeled by Ly), which contains several virus-like particles, is found in the cytoplasm of the adjacent SCs. Panel B shows a virion located extracellularly between an infected neuron and its SC, where the invaginated plasma membrane of the infected neuron is covered with a layer of coating decorations (larger arrow). Panels in middle and bottom rows show HEV transfer by use of large smooth-surface vesicles, which is found to occur in neuronal perikaryal specializations. In Panels C and D, the neuronal projections are seen arising from the neuronal cell body and appear as microvillus-like structures (asterisks). Panels E and F show cross-sectioned neuronal projections (asterisks), which are embedded within the cytoplasm of SCs without continuity with the neuronal cell bodies.
