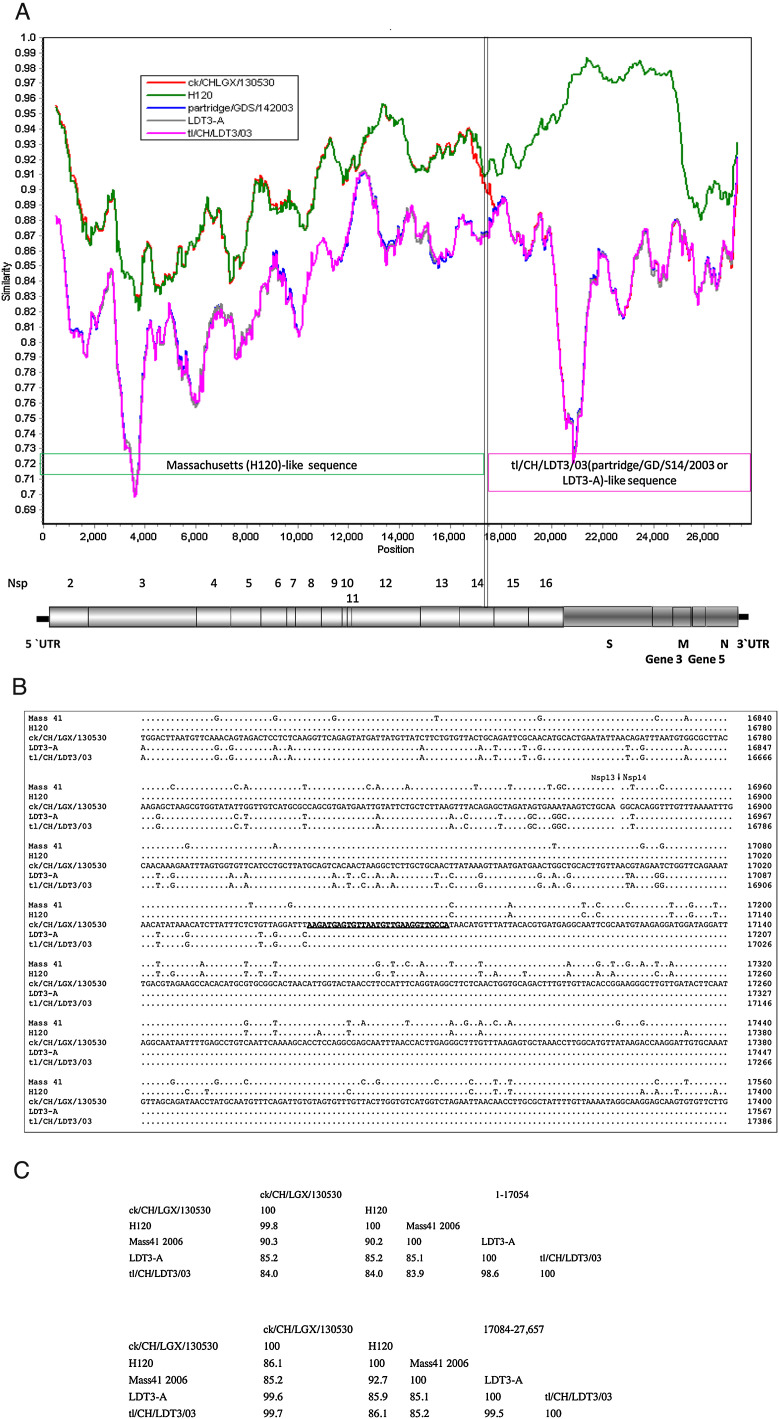
Fig. 1.
Recombination analysis of the IBV ck/CH/LGX/130530 isolate. Similarity plot using Mass 41 as the query sequence (A). The dotted lines show the deduced recombination breakpoints. The hollow arrows show the different fragments and their colors are the same as those of the parental viruses. The numbers show the nucleotide positions of the corresponding fragments in the genome of the ck/CH/LGX/130530 isolate. Multiple sequence alignment of the predicted breakpoint and flanking sequences among IBV Mass 41, H120, ck/CH/LGX/130530, tl/CH/LDT3/03 and LDT3-A strains (B). The numbers on the right of each alignment show the nucleotide positions in the genome of each virus. The sequences of ck/CH/LGX/130530 are listed, and only the nucleotides differing from those of ck/CH/LGX/130530 are depicted. The region where the template switches (breakpoint) have taken place is underlined. The deleted nucleotides are indicated by a -. GenBank accession numbers are in bold. The GenBank accession numbers are Mass 41 (AY851295), H120 (FJ888351), and partridge/GD/S14/2003 (AY646283). Percentages of nucleotide sequence identity among Mass 41, H120, ck/CH/LGX/130530, tl/CH/LDT3/03 and LDT3-A strains (C). The percentages of nucleotide sequence identity of the corresponding gene fragments are indicated.