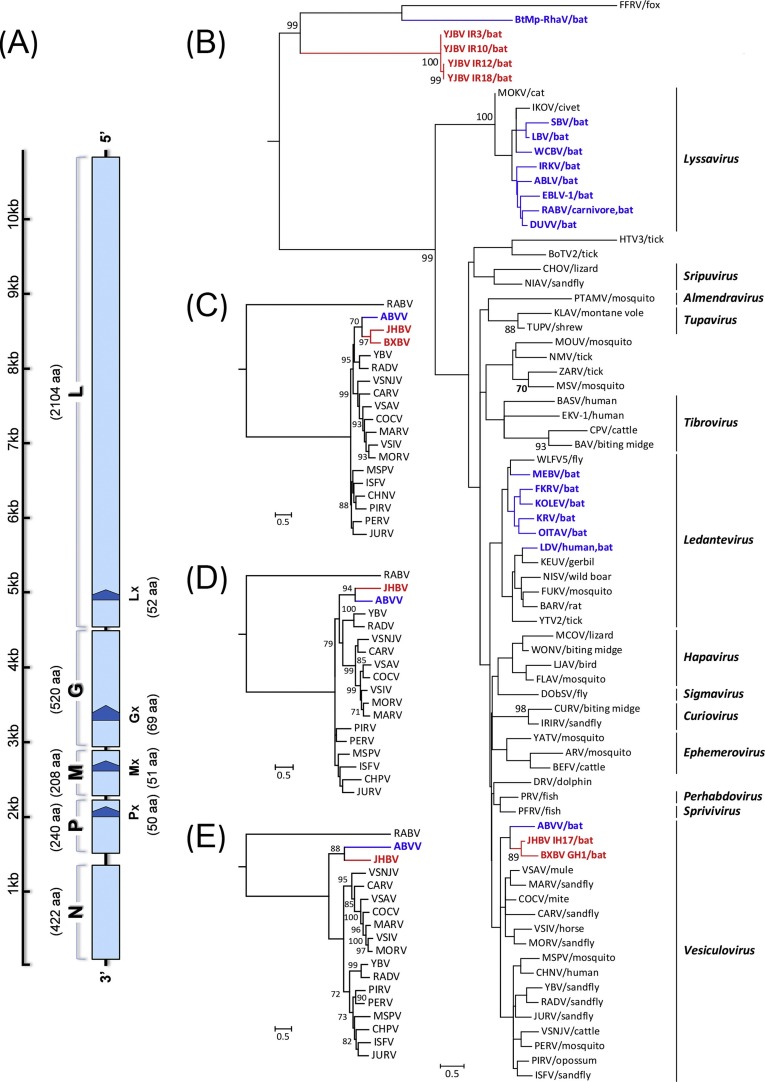
Fig. 2.
(A) Schematic genome organization of JHBV with five canonical ORFs (3′-N-P-M-G-l-5′, light blue) and four overlapping accessory ORFs (≥150 nt, Px, Mx, Gx and Lx, dark blue) being predicted. Phylogenetic tree of rhabdoviruses was generated based on 252-nt sequences of the L gene (B); and trees of vesiculoviruses were generated based on 1591-nt sequences of L gene (C), complete sequences of N (D) and G (E) gene, with the RABV as outgroup. The evolutionary history was inferred in MEGA7 by using the Maximum Likelihood method based on the General Time Reversible model. Bootstrap support values of 1000 replicates (≥70%) are shown and the scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site. The sequences obtained in the present study are identified in red, and other bat-associated rhabdoviruses in blue. Definitions of virus abbreviations and their GenBank accession numbers are listed in Table S3. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)