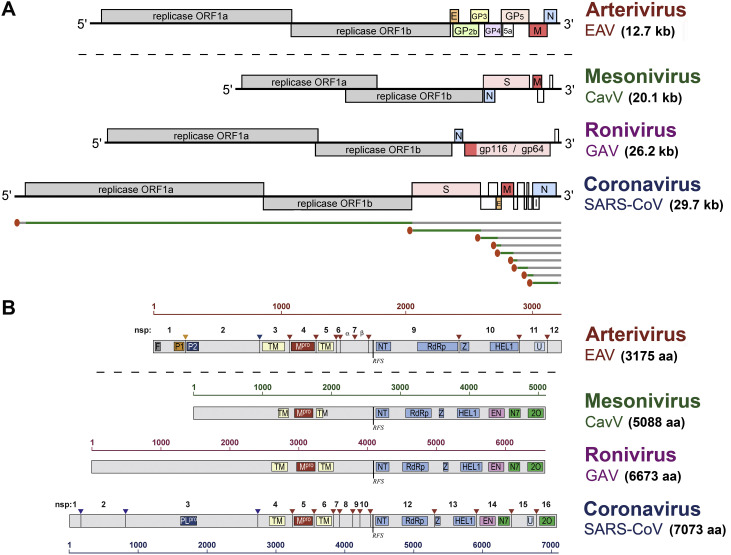
Fig. 1.
Nidovirus genome organization and the core replicase domains. (A) Genome organization of representatives of the four major nidovirus lineages (CavV, Cavally virus; GAV, gill-associated virus; note that the EAV genome is drawn to a different scale). For each genome, the known open reading frames (ORFs) are indicated with the replicase ORFs 1a and 1b depicted in grey and structural protein genes depicted in different colours. ORFs encoding ‘accessory proteins’ (in SARS-CoV) or poorly characterized products are depicted in white. To illustrate the principle of subgenomic mRNA synthesis, as employed by all nidoviruses, the nested set structure and composition of the mRNAs is summarized for SARS-CoV, with the common 5′ leader sequence indicated in red and the translated part of the genome and each of the subgenomic mRNAs depicted in green. See main text for more details. (B) Domain organization of the pp1ab replicase polyprotein for the four major nidovirus lineages (note that the AV protein is drawn to a different scale). Proteolytic cleavages and non-structural protein numbering are indicated for EAV and SARS-CoV. The scheme highlights the conservation of the so-called nidovirus ‘core replicase’, consisting of the ORF1a-encoded main protease (Mpro) flanked by two transmembrane (TM) domains, followed by the ORF1b-encoded NiRAN nucleotidyl transferase (NT), RNA polymerase (RdRp), zinc binding domain (Z) and superfamily 1 helicase (HEL1). Accessory (papain-like) protease domains and their cleavage sites are indicated for EAV and SARS-CoV (P1, P2, PLpro). The zinc-finger domain (F) in EAV nsp1 that is crucial for subgenomic mRNA synthesis (see text) is also highlighted. The C-terminal part of pp1ab encodes a number of enzymatic domains that are not strictly conserved among all nidovirus lineages: U, endoribonuclease, conserved in vertebrate nidoviruses; EN, exoribonuclease (ExoN) conserved in nidoviruses with genome sizes >20 kb (see text); N7- and 2′-O methyl transferases (N7 and 2O) involved in cap modification (not identified in AVs).