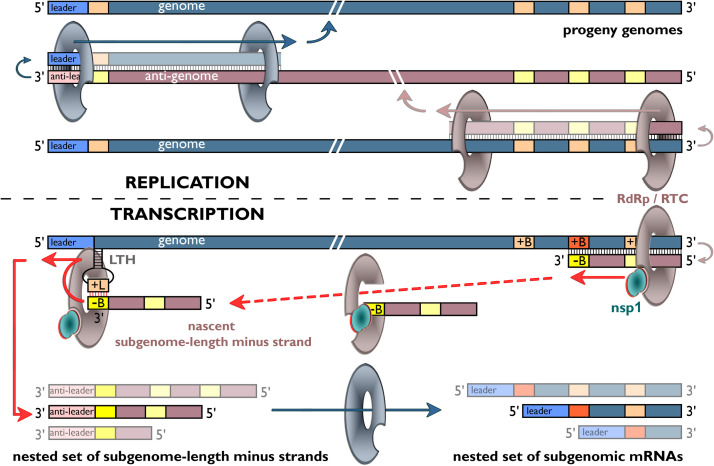
Fig. 5.
Nidovirus RNA synthesis. Model for replication and transcription using a hypothetical genome encoding three sg mRNAs. The top half of the scheme depicts the replication of the genome from a full-length minus-strand intermediate (antigenome). The bottom half illustrates how minus-strand RNA synthesis can be attenuated at a body TRS (+B), after which the nascent minus strand, having a body TRS complement (−B) at its 3′ end, is redirected to the leader TRS (+L) near the 5′ end of the genome. Guided by a base-pairing interaction between the −B and +L sequences, RNA synthesis is resumed to add the anti-leader sequence to each nascent subgenome-length minus strand. Subsequently, the latter serves as template to produce a sg mRNA. The RdRp complexes engaged in replication and transcription may differ, as transcription-specific regulatory protein factors, like EAV nsp1, have been described (Nedialkova et al., 2010). For further details, see text. Adapted from (Snijder and Kikkert, 2013).