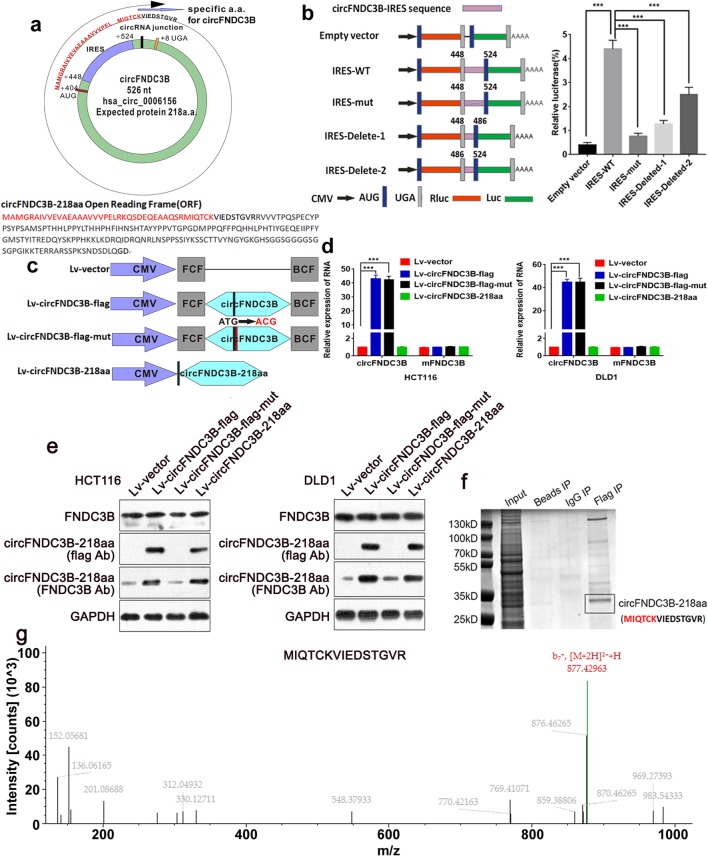
Fig. 3.
Evaluation of the coding ability of circFNDC3B. a Upper panel, the putative open reading frame (ORF) in circFNDC3B. The ORF implied that it took more than one whole circle of circFNDC3B. Lower panel, the sequences of putative ORF are shown. b The putative IRES activity of circFNDC3B was tested. Left panel, IRES sequences in circFNDC3B or its different truncation/mutation were cloned between the Rluc and Luc reporter genes with independent start (AUG) and stop (UGA) codons. Right panel, the relative luciferase activity of Luc/Rluc in the above vectors was tested. c Four vectors were constructed. Lv-vector; Lv-circFNDC3B-flag: flag-labeled circFNDC3B sequence was cloned into a CMV-induced expression vector; Lv-circFNDC3B-flag-mut: flag-labeled circFNDC3B sequence with start codon mutant (ATG → ACG) was cloned into a CMV-induced expression vector; Lv-circFNDC3B-218aa: flag-labeled circFNDC3B-218aa sequence was cloned into a CMV-induced expression vector. FCF and BCF are sequences which could circularize the sequence of circRNA. d Relative RNA expression of circFNDC3B and linearFNDC3B were detected by qRT-PCR. e The expression level of flag-label circFNDC3B-218aa and FNDC3B were detected by Western blotting analysis. f The lysates from indicated cells were separated by SDS-PAGE. Protein bands near 25 kDa were excised manually and summited for identification by LC-MS/MS. g circFNDC3B-218aa junction-specific peptide (MIQTCKVIEDSTGVR) was identified. ***P < 0.001