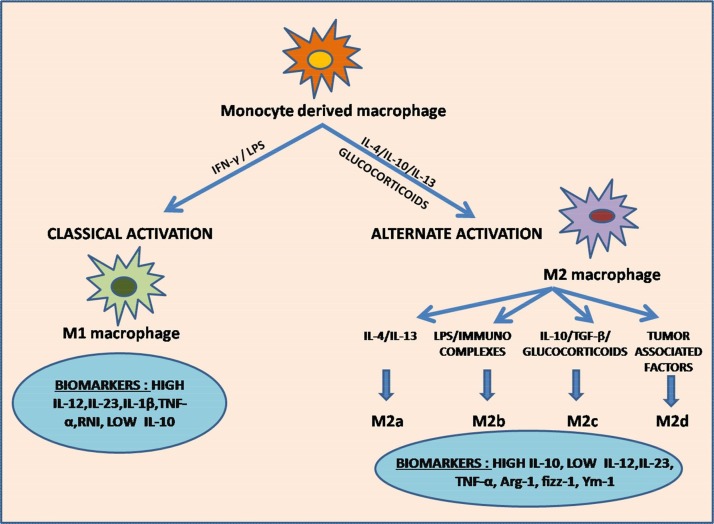
Fig. 1.
Classical and Alternate pathway of Macrophage polarization.
The figure depicts the pathways involved in macrophage polarization in response to signals received from micro-environment. Classical activation of M1 macrophages is induced by LPS/IFN-γ exposure. Activated M1 macrophages promote enhanced secretion of M1 chemokines, Th1 response elements, i-NOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase) dependent reactive nitrogen intermediates (RNI), high levels of IL-12, IL-23 IL-1β and TNF-α, and low levels of IL-10, which exert pro-inflammatory and cytotoxic effects. They are also involved in tumor suppression and immunostimulation. Alternately activated M2 macrophages are stimulated by IL-4, IL-10, IL-13 and glucocorticoids. IL-4 and IL-13 activates M2a subtype. Presence of immunocomplexes and LPS activates M2b subtype. M2c subtype is induced by IL-10, TGF-β and glucocorticoids. Presence of tumor associated factors triggers the activation of M2d subtype. Activated M2 macrophages enhance the secretion of IL-10 and reduces the secretion of IL-12 and IL-23 due to which they exert anti-inflammatory effects and roles in tissue repair and wound healing. M2d subtype is the prime constituent of TAMs (tumor associated macrophages) and hence promote tumor growth.