Figure 1.
Laboratory-Evolved TMP-Resistant E. coli Exhibit Multiple Transcriptomic Changes
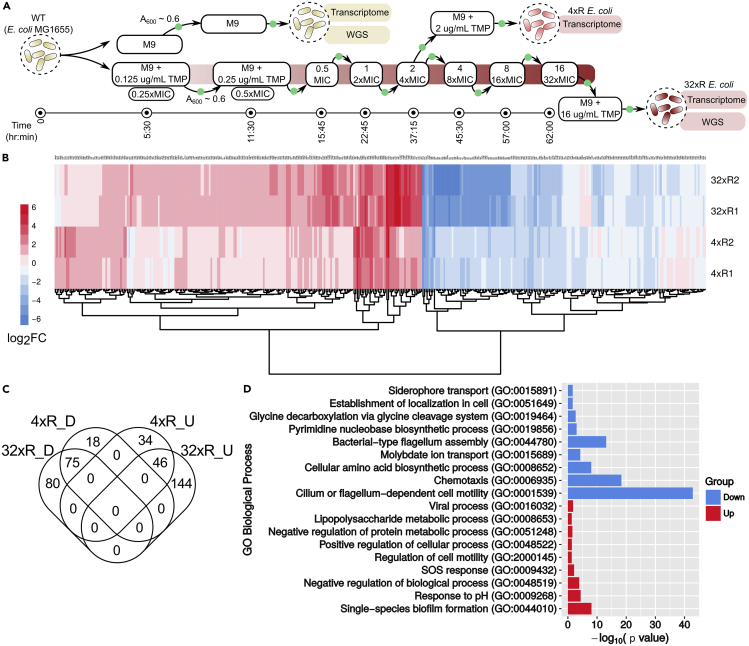
(A) Evolution of TMP-resistant 32xR E. coli: TMP-sensitive WT E. coli were adapted to TMP in a stepwise manner over 2.5 days. The adaptation was initiated by growing WT in sub-inhibitory (0.25xMIC) TMP concentration of 0.125 μg/mL to A600 ~ 0.6 (green filled circle) followed by inoculation in 2x TMP (0.25 μg/mL). This was done iteratively by doubling the concentration in each step till E. coli adapted to 16 μg/mL TMP. Line at the bottom indicates time after which the culture reached A600 ~ 0.6 in a particular concentration.
(B) log2FC values of 397 DEGs in biological replicates of 4xR and 32xR E. coli. The FC of a gene is the mean of the FC of biological replicates of 4xR or 32xR. In general, FC is seen to be higher in 32xR as compared with 4xR.
(C) Common DEGs in 4xR and 32xR: 75 and 46 genes were commonly downregulated (D) and upregulated (U), respectively.
(D) Gene Ontology (GO) Biological Process enrichment of DEGs in 32xR E. coli: Biofilm formation, response to pH, and SOS response were significantly enriched in upregulated DEGs (red), whereas motility and amino acid biosynthesis were enriched in downregulated DEGs (blue).