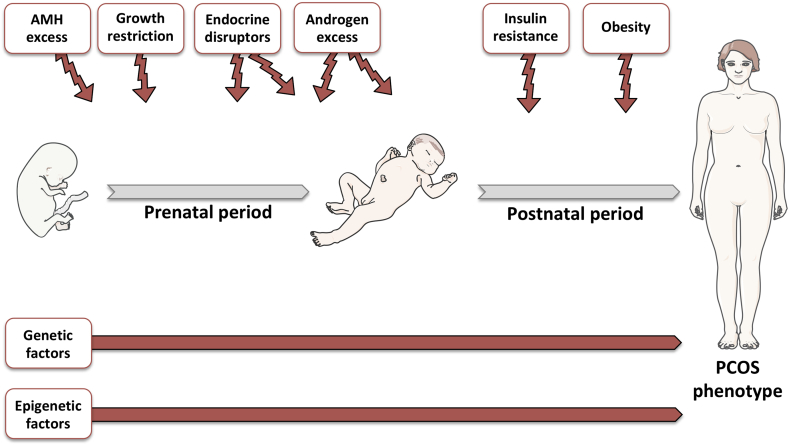
Figure 1.
Potential pathogenic factors of PCOS. During gestation, multiple factors including increased AMH levels, growth restriction, endocrine disruptors such as BPA, and androgen excess may predispose to the development of a PCOS-like phenotype in adulthood. During the postnatal period, exposure to endocrine disruptors and androgen excess and the development of obesity and insulin resistance are considered pathogenic factors that may also cause PCOS. Genetic and epigenetic factors may also increase the risk of developing PCOS. The figure was designed using tools provided by Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com).