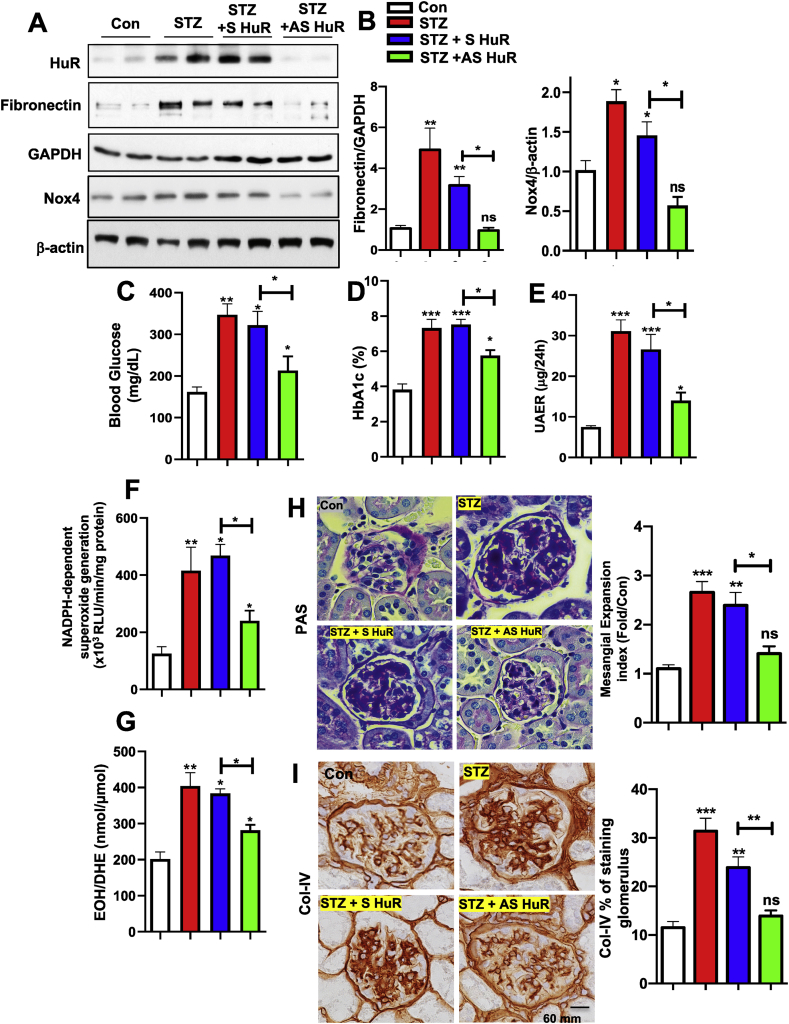
Figure 5.
Inhibition of HuR protein in diabetic animals ameliorates matrix protein accumulation, renal function and histopathology. The expression of HuR, Nox4 and fibronectin (A) was assessed by western blotting assay in kidney cortical lysates from control, STZ-induced, STZ + sense (S) RNA against HuR, and STZ + antisense (AS) RNA against HuR mice. GAPDH and β-actin were used as loading controls. Band intensities were quantified by Image J, normalized to loading controls, and presented in B. (C–G), hyperglycemia, renal function and ROS were improved after HuR antisense treatment. Blood glycose (C) and HbA1c ratio (D) were measured in all groups. Renal function was assessed by measuring protein albumin levels in 24 h of urea collection. ROS levels were present as the levels of superoxides, measured by lucigenin chemiluminescence (F) and HPLC analysis (G). Representative PAS staining (H) and collagen type IV (Col-IV) (I) in kidney sections from the above four groups were shown here (scale bar, 60 μm). Pixel intensities were quantified by Image J. normalized to control samples, and present in H and I for PAS staining and Col-IV, respectively. Histograms represented the mean ± S.E of three to five mice in one group. ∗, p < 0.05; ∗∗, p < 0.01, ns for non-significant, in comparison with control or as indicated. One-way ANOVA was used for comparison between multiple groups.