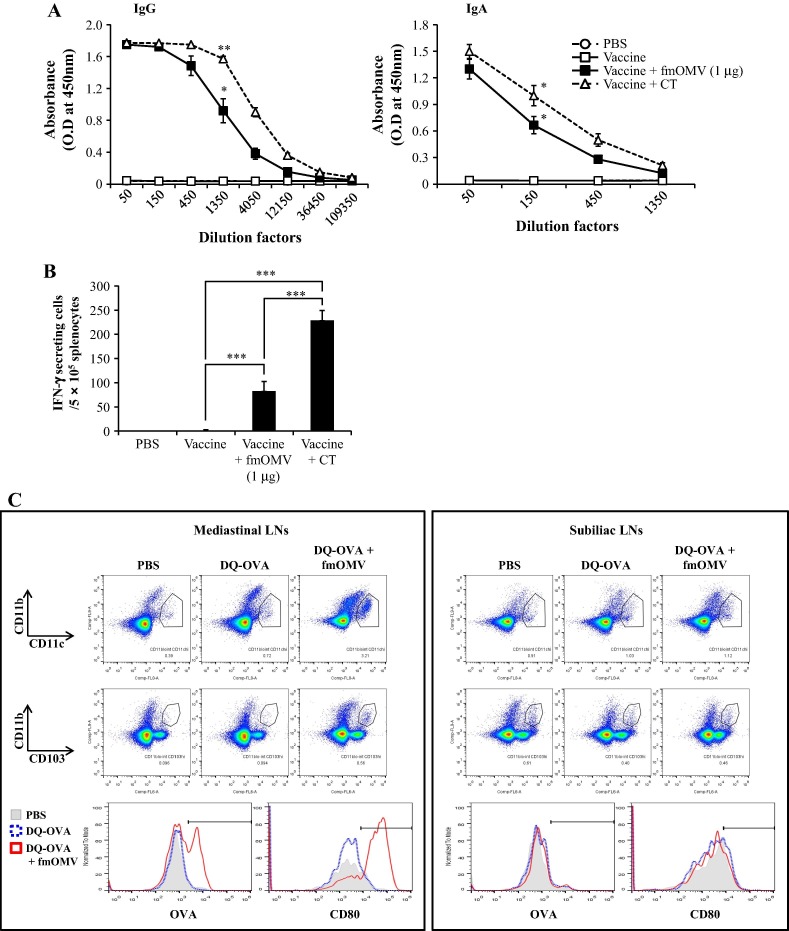
Fig. 3.
Co-administration of fmOMV activates respiratory CD103 + DCs and increases local antibody and T cell responses in the lungs. Mice (n = 6) were immunized intranasally with a seasonal influenza vaccine in the presence or absence of OMV (1 μg). Two weeks after the booster injection, IgG and IgA ELISAs against the vaccine antigen were performed with BALF samples (A). An IFN-γ ELISPOT assay against UV-inactivated pH1N1 virus was performed with total lung cells (B). Twenty-four hours after intranasal injection of DQ-OVA, mediastinal and subiliac LNs were harvested and the cells were analyzed for the expression of the indicated markers using flow cytometry (C). Data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results (A–C) and presented as the mean ± SEM (A and B). ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05.