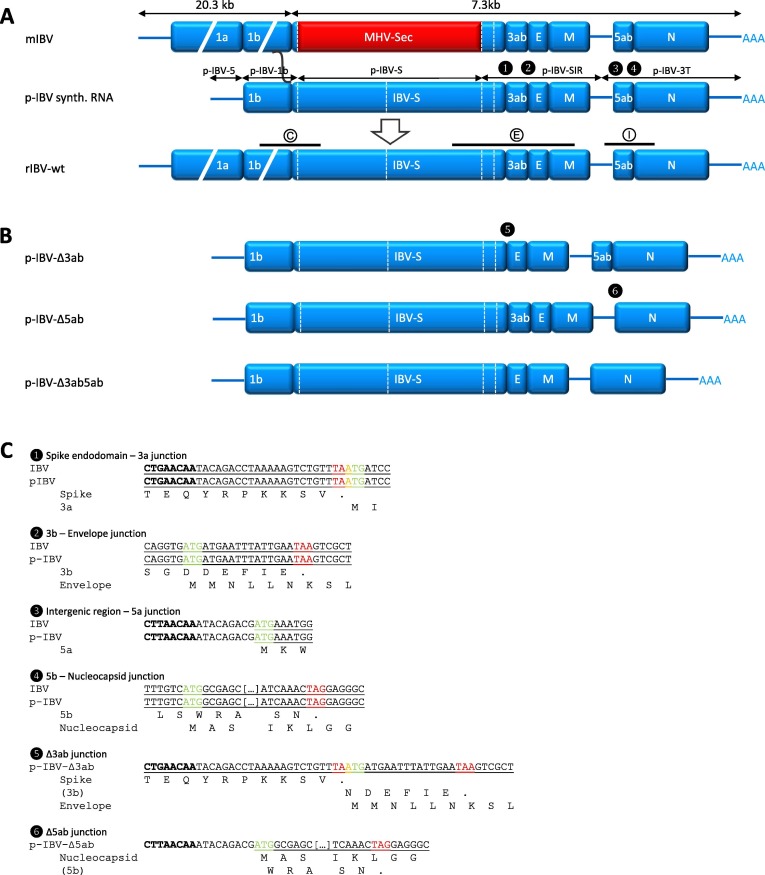
Fig. 1.
Schematic overview of targeted RNA recombination principle and donor plasmids. (A) Schematic overview of step 2 in the targeted RNA recombination method for generating recombinant (r)IBV wild type (wt) [15]. IBV sequences are represented in blue, MHV sequences in red. pIBV-derived synthetic donor RNA is indicated by a black composite line above which the parts derived from specific sub-plasmids are indicated. PCR amplicons used to confirm the recombination (set C) and the status of gene 3ab (set E) and gene 5ab (set I) are depicted as black bars drawn to scale above the rIBV-wt genome, with encircled letters referring to the primer sets in Table 2. (B) Schematic layout of the donor plasmids p-IBV-Δ3ab, -Δ5ab and -Δ3ab5ab used in targeted RNA recombination to generate rIBV-Δ3ab, -Δ5ab and -Δ3ab5ab, respectively. (C) Nucleotide sequences of the gene and plasmid junctions are marked with numbers corresponding to the numbers in black circles in the schematic donor plasmid layout in (A) and (B). Transcription regulatory sequences are in bold. Nucleotide sequences are indicated for wild type IBV and donor plasmids p-IBV, p-IBV-Δ3ab and p-IBV-Δ5ab. Start codons are highlighted in green, stop codons in red, and start-stop overlaps in yellow. ORFs are underlined, overlapping ORFs are underlined with a bold line, and ORF translations are indicated as amino acids below the nucleotide sequences if applicable. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)