Fig. 1.
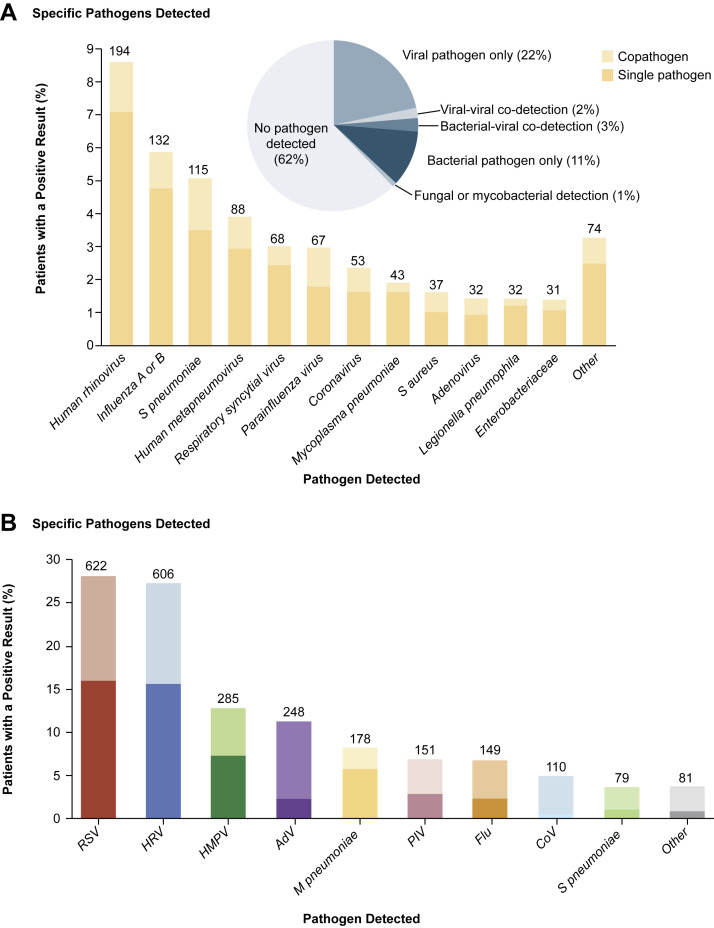
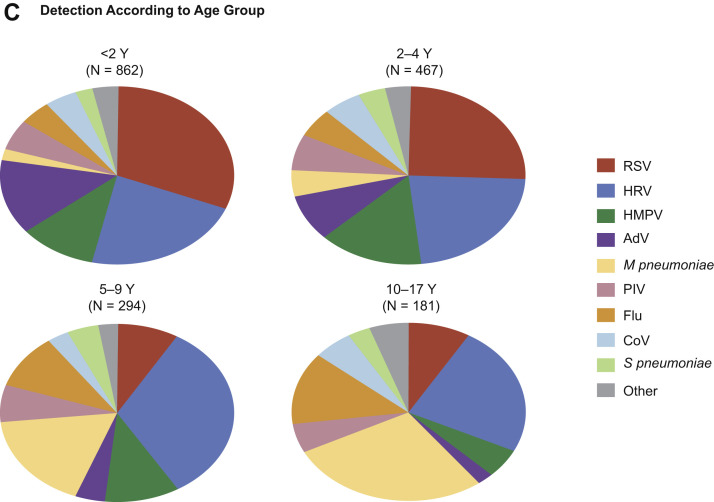
(A) Numbers (above the bars) and percentages of all adults in whom a specific pathogen was detected in the adult component of the EPIC study. The proportions of viral, viral-viral, bacterial-viral, bacterial, fungal or mycobacterial pathogens detected, and no pathogen detected are shown in the pie chart. (B) Numbers (above the bars) and percentages of all children in whom a specific pathogen was detected in the pediatric component of the EPIC study. (C) Proportions of pathogens detected, according to age group in the pediatric component of the EPIC study.
(From [A] Jain S, Self WH, Wunderink RG, et al. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 2015;373:420, with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society; and [B, C] Jain S, Williams DJ, Arnold SR, et al. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. children. N Engl J Med 2015;372:840; with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society.)