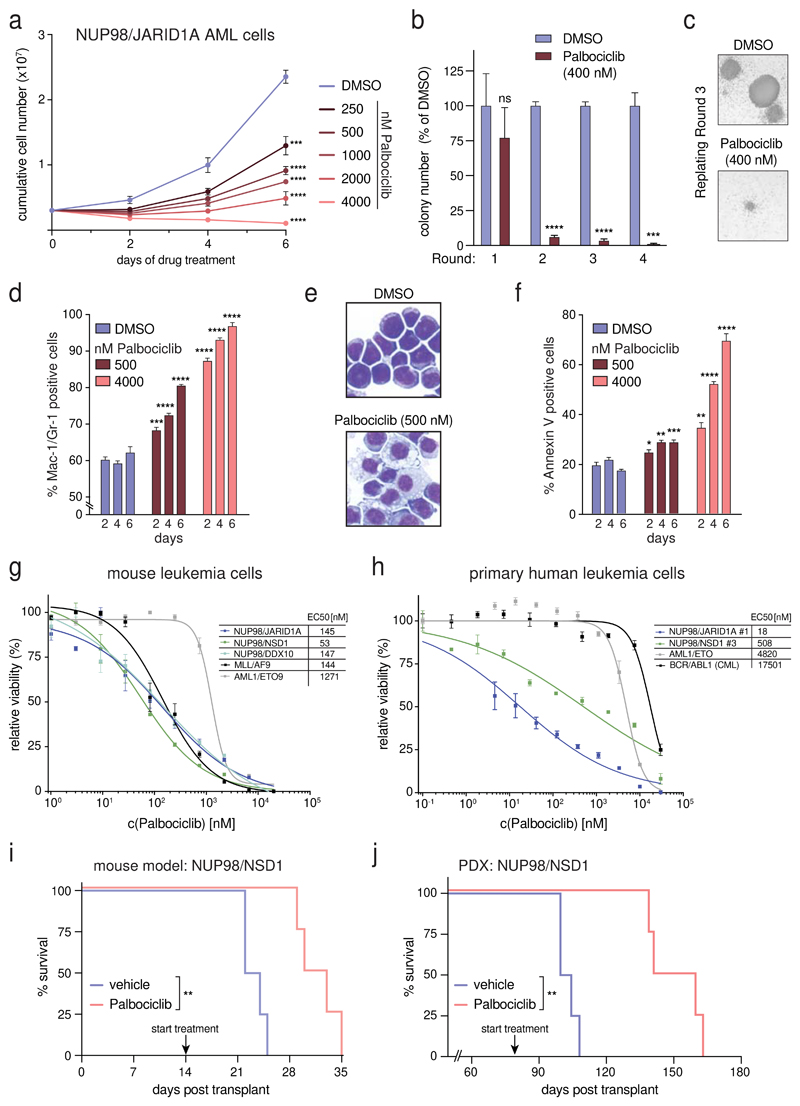
Figure 6. NUP98-fusion-protein-driven leukemia is highly sensitive to pharmacological CDK4/CDK6 inhibition.
(a) Proliferation curves of murine NUP98/JARID1A-expressing leukemia cells in the presence of indicated concentrations of Palbociclib. (mean ± s.d. n = 3). (b) Colony formation assay of murine NUP98/JARID1A-expressing leukemia cells in the presence of DMSO or Palbociclib. Colony numbers were normalized to DMSO (mean ± s.d. n = 3). (c) Representative image of colonies in the presence of DMSO or Palbociclib after three rounds of replating. (d) Flow cytometric analyses of Mac-1/Gr-1 surface marker expression in NUP98/JARID1A-expressing AML cells treated with indicated concentrations of Palbociclib (mean ± s.d. n = 3). (e) Representative Cytospin images illustrating the morphology of NUP98/JARID1A-expressing AML cells 7 days after DMSO or Palbociclib treatment. (f) Flow cytometric analyses of AnnexinV expression in NUP98/JARID1A-expressing leukemia cells treated with indicated concentrations of Palbociclib (mean ± s.d. n = 3). (g,h) Dose-response curves of Palbociclib-mediated growth inhibition of murine leukemia cells (g) and primary patient cells (h) driven by different fusion proteins (mean ± s.e.m. n = 3). (i) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of C57BL/6 Ly5.1 recipients transplanted with murine NUP98/NSD1-driven leukemia cells after vehicle or Palbociclib treatment (50mg/kg, n = 4). (j) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of NSG mice transplanted with NUP98/NSD1-PDX AML cells after vehicle or Palbociclib treatment (50mg/kg, n = 4).