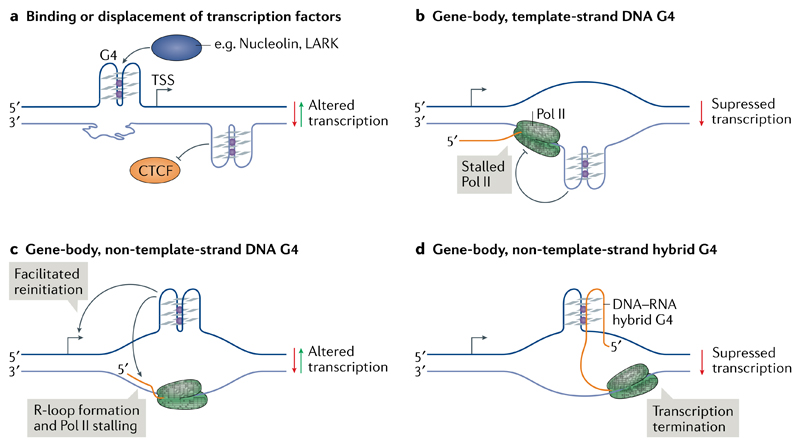
Fig. 4. Models of G-quadruplex involvement in transcription.
a | DNA G-quadruplexes (G4s) upstream of the transcription start site (TSS) or in the gene body could bind or displace transcription factors, resulting in altered transcription. b | During transcription elongation, the separation of DNA strands in the transcription bubble may result in the formation of G4s in gene bodies. G4 formation on the template strand can block the progression of RNA polymerase II (Pol II). c | Gene-body G4s on the non-template strand may facilitate transcription re-initiation. Conversely, such G4s may favour the stable association of nascent RNA (orange) with the template DNA, resulting in the formation of RNA–DNA hybrids known as R-loops and in Pol II stalling. d | Formation of DNA–RNA hybrid G4s between the non-template DNA and the nascent RNA can lead to premature transcription termination.