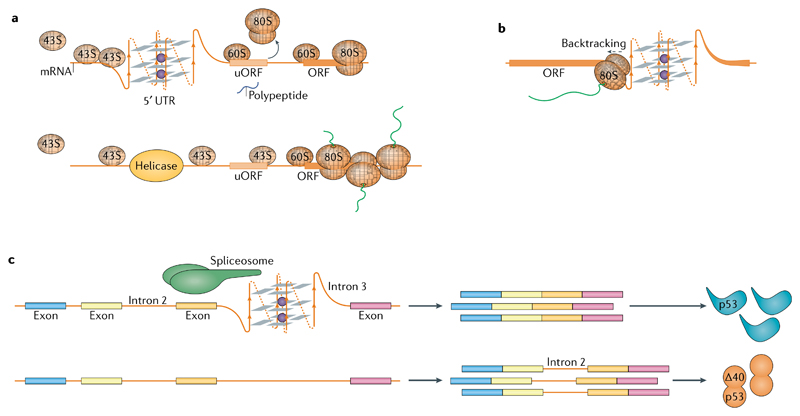
Fig. 5. G-quadruplexes in RNA biology.
a | Formation of RNA G-quadruplexes (G4s) impedes scanning of the 5′ untranslated region (UTR) by 43S ribosomes and leads to translation initiation at an upstream open reading frame (uORF) at the expense of translation of the main ORF (top). Helicases, such as DHX36 or DHX9, resolve the G4s and facilitate translation of the main ORF (bottom). b | The 80S ribosomes engaged in translation elongation stall 6–7 nucleotides prior to a G4 within the ORF. Stalling can cause ribosome backtracking and synthesis of an alternative peptide. c | Recognition of RNA G4s by spliceosome-associated RNA-binding proteins directs splicing of nearby introns, for example the second intron of p53.