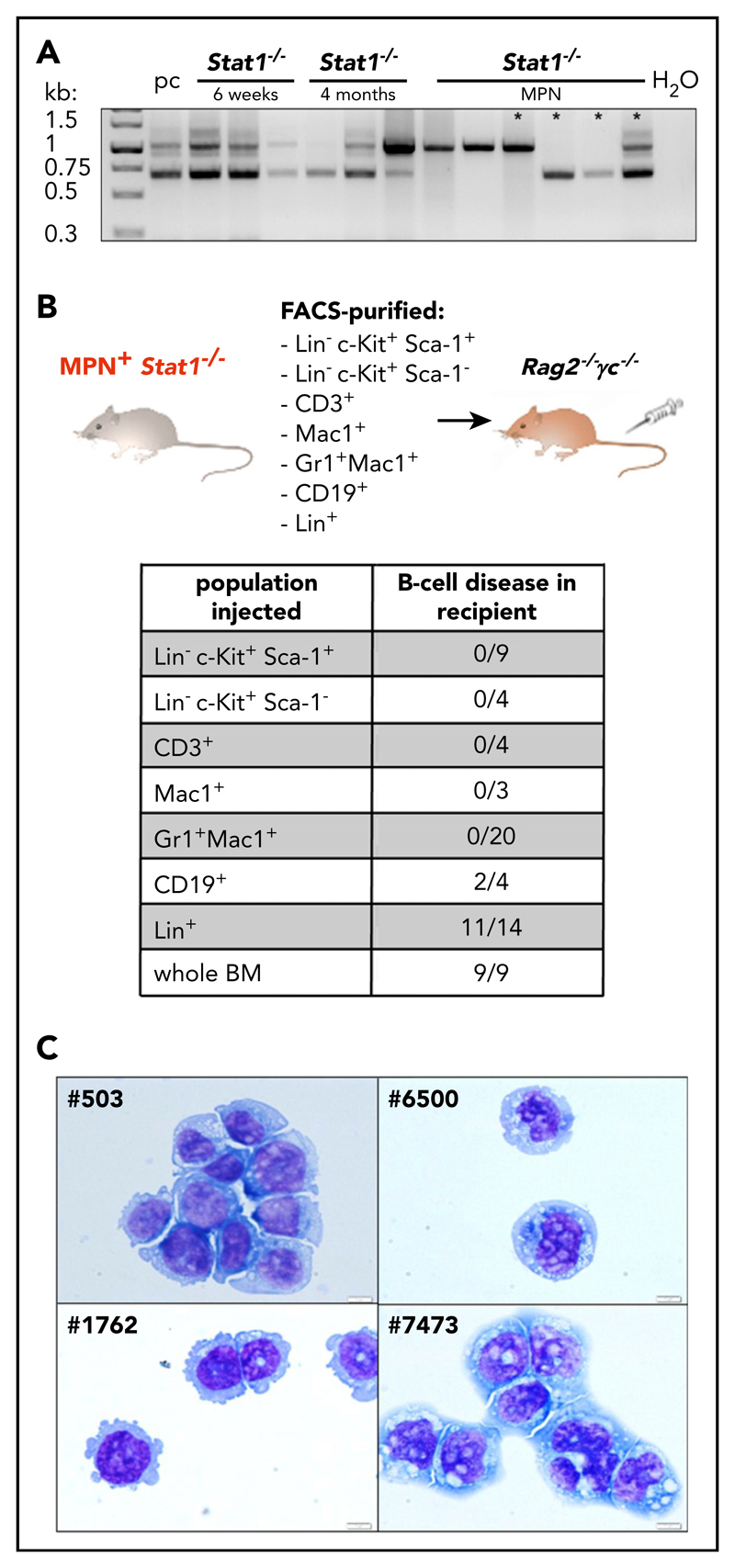
Figure 3. Stat1−/− mice recapitulate the phenotype of coexisting MPN and B-cell transformation.
(A) BM of Statl −/− mice with 6 weeks of age (n = 3), 4 months of age (n = 3), and Statl −/− MPN+ mice (n = 6) was analyzed for D-J rearrangement of the IgH gene. Pc, polyclonal B cells (derived from splenocytes of a wt mouse). Asterisks denote samples of those mice, whose B-cell clonality was followed in subsequent transplantations (outlined in supplemental Figure 5C). (B) BMs or spleens of MPN+ Statl −/− mice were fractionated into LSK (Lin−Sca-1+c-Kit+), progenitors (Lin−c-Kit+ Sca-1), CD3+, Mad+, Gr1+Mac1+, CD19+, and Lin+ cells and intravenous injected into Rag2−/− γc/ mice. Table shows incidence of B-cell disease in recipient mice that had received individual populations or whole BM. (C) Cytospins of Statl −/− B-cell lines: #503, #1762, #6500 and #7473. Original magnification: 40X. Scale bar, 10 μm.