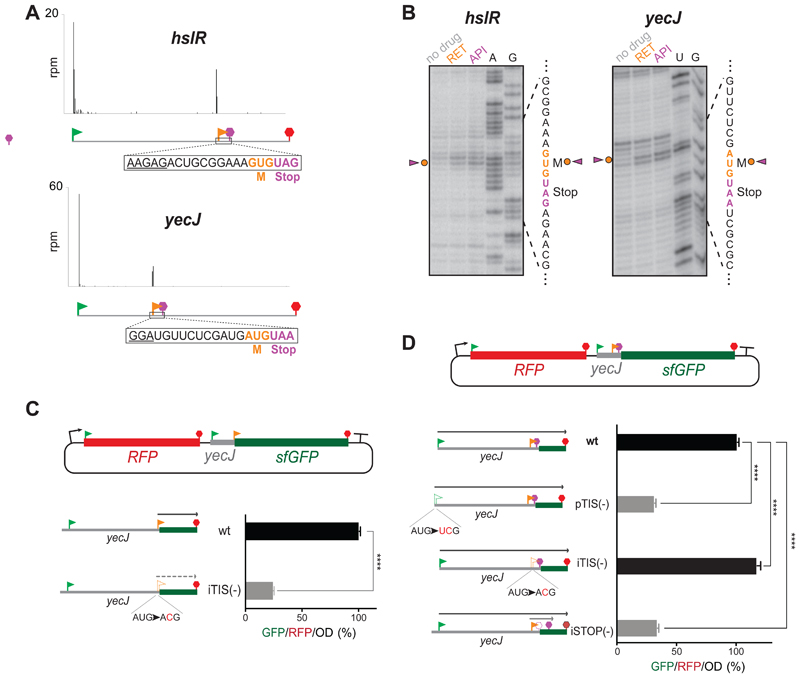
Figure 5. Start-Stops within E. coli genes.
(A) Representative Ribo-RET profiles revealing start-stops. The SD-like sequences are underlined.
(B) Toeprinting analysis shows ribosomes stalled at the start codons of the start-stop sites in response to the presence of initiation (RET) and termination (API) inhibitors. The start and stop codons of the start-stop sites are indicated by orange and purple characters, respectively.
(C) The start codon of the yecJ start-stop can direct initiation of translation in vivo. sfGFP expression in the RFP/sfGFP reporter is directed by the start codon of the yecJ start-stop (orange flag). The relative translation efficiency was estimated by measuring GFP/RFP/OD (%) ratio. The expression of sf-gfp is severely abrogated by a mutation that disrupts the start-stop initiation codon [iTIS (-)]. The values represent the standard deviation from the mean in technical replicates (n=3). Two-tailed unpaired t-test.
(D) Start-stop impacts expression of the yecJ gene. The expression of the YecJGFP chimeric protein is controlled by yecJ pTIS (green flag) (gfp sequence is in 0-frame relative to pTIS). The reporter expression increases by ~16% when the start codon of the start-stop site is disrupted by a mutation [(iTIS(-)]. Mutating the stop codon of the start-stop site expands the length of the translated OOF coding sequence and results in severe inhibition of the main frame translation. The error bars represent standard deviation from the mean in technical triplicates (n=3). Two-tailed unpaired t-test.
See also Figure S5 and Table S2.