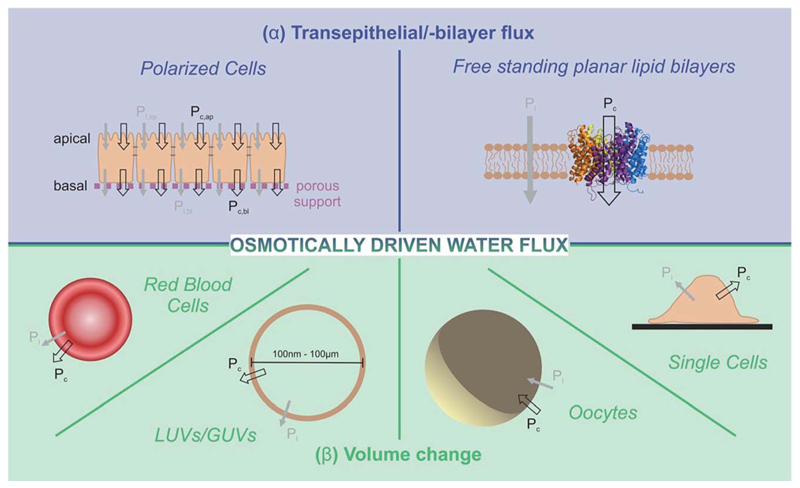
Fig. 4.
Two different approaches allow estimations of integral osmotic water permeability P f: (α) continuous flux experiments through a confluent cell monolayer or a free standing planar lipid bilayer (blue background), or (β) volume adaptation of cells or vesicles after an osmotic challenge (green background). In both cases the overall permeability P f is the sum of the permeabilities p f,l and P f,c of the lipid matrix and water conducting channels, respectively. The measurement systems include artificial free standing planar lipid bilayers as well as large or giant unilamellar vesicles (LUVs/GUVs) on the one hand and erythrocytes, oocytes, confluent cell monolayers or single cells on the other hand.