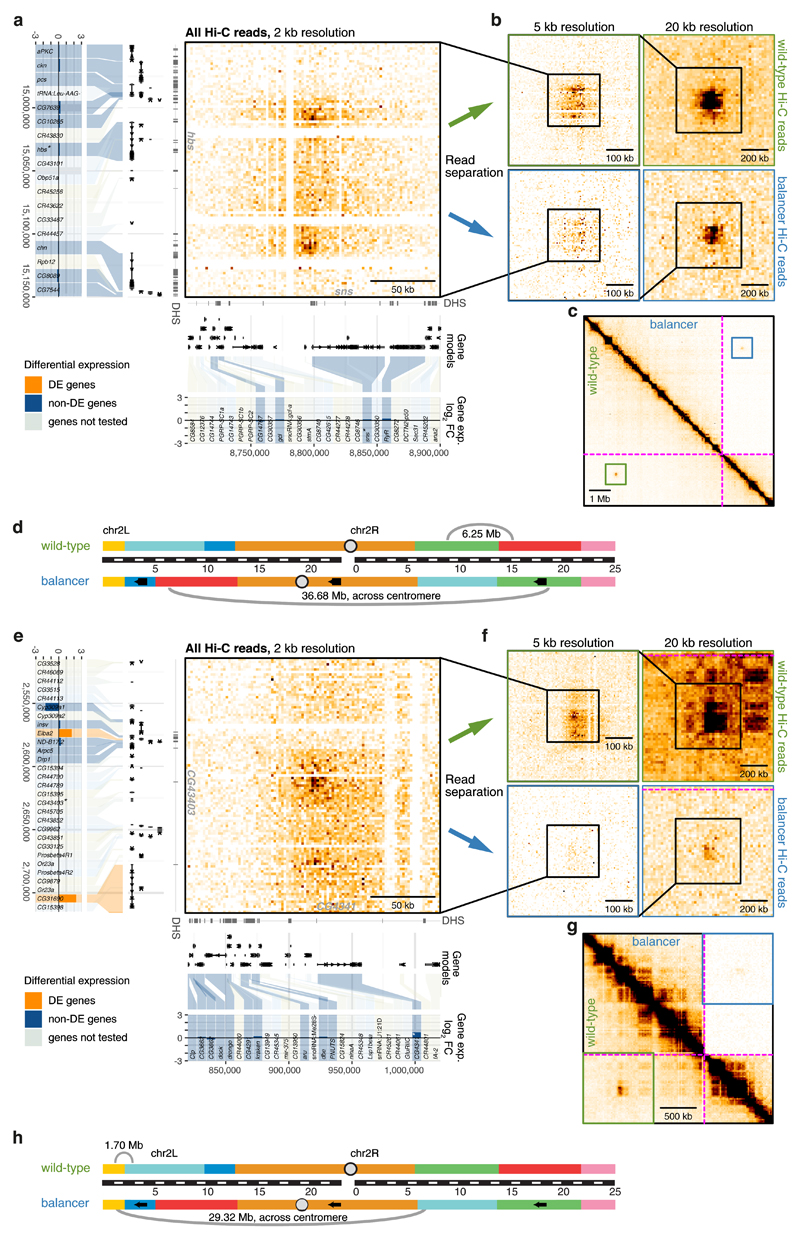
Figure 5. Loss of long-range chromatin loops has little impact on gene expression.
a, e, Hi-C contact map (2 kb resolution, all Hi-C reads) showing a long-range loop between hbs (left) and sns (bottom) (a) or CG43403 (left) and CG4341 (bottom) (e). The location of DNase hypersensitive sites (DHS), gene models, and differential gene expression (balancer/wild-type; log2 fold change) are shown. Differentially expressed (DE) genes in orange, non-DE genes in blue and non-tested genes (lowly expressed or lacking SNVs) in grey. b, f, Zoomed-in wild-type (top) and balancer (bottom) Hi-C contact maps at 5 kb (left) and 20 kb (right) resolution showing a slight (b) or strong (f) decrease in the strength of long-range loops. c, g, Zoomed-out Hi-C contact map showing the location of the long-range loops between sns and hbs (c) and CG4341 and CG43403 (g) in the wild-type (bottom left) and balancer (top right) haplotypes. The location of inversion breakpoints is indicated by purple dotted lines. d, h, Cartoon depicting the location, and distances, of both loops on chromosome 2 in wild-type (top) and balancer (bottom) haplotypes with respect to the inversion breakpoints.