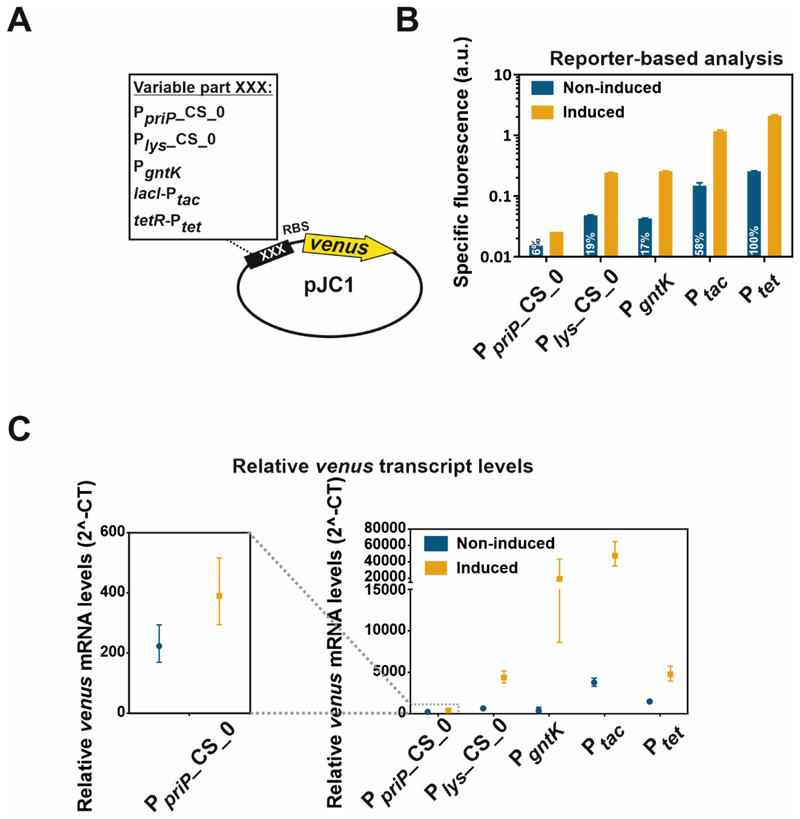
Figure 3. Comparison of counter-silencing constructs with established expression systems.
A) For the comparison of the counter-silencer constructs Plys_CS_0 and PpriP_CS_018 as well as the native GntR target promoter PgntK18 with the established expression systems Ptac and Ptet, all of the different promoters were cloned into the plasmid pJC1 and fused to the reporter gene venus via a consistent linker containing a ribosomal binding site (RBS; AGGAG47). C. glutamicum wild type cells harbouring the plasmid-based constructs were cultivated in a microtiter cultivation system under inducing and non-inducing conditions depending on the particular promoter construct: PpriP_CS_0 and Plys_CS_0: +: 100 mM glucose, -: 100 mM gluconate; PgntK: +: 100 mM gluconate, -: 100 mM glucose; Ptac: +: 100 mM glucose + 100 µM IPTG, -: 100 mM gluconate + 0 µM IPTG; Ptet: +: 100 mM glucose + 235 nM ATc, -:.100 mM gluconate + 0 nM ATc B) Reporter outputs of the native GntR target promoter PgntK as well as PpriP- and Plys-based counter-silencer constructs (PpriP_CS_0; Plys_CS_0) in comparison to the established expression systems Ptac and Ptet after five hours of cultivation. All strains were pre-cultivated in CGXII containing 100 mM gluconate. Bars show the mean and error bars the standard deviation of specific fluorescence of biological triplicates. Specific fluorescence was calculated by dividing the Venus fluorescence signal by the backscatter signal per time point63. Indicated numbers represent the percentage of the background expression level of Ptet. C) Promoter-derived relative venus transcript levels measured by quantitative real-time PCR after five hours of cultivation under non-inducing and inducing conditions. Symbols represent the means and error bars the range of relative venus mRNA levels measured in biological and technical duplicates. All strains were pre-cultivated under non-inducing conditions.