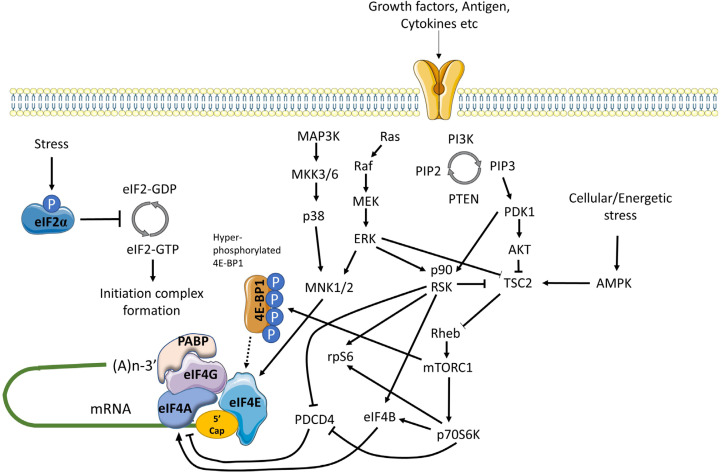
Figure 3.
Positive and negative regulation of mRNA translation initiation by signaling pathways. mRNA translation is promoted by PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 and MAPK signaling. mTORC1 is activated via repression of TSC2-mediated conversion of Rheb-GTP to inactive Rheb-GDP. mTORC1 promotes the hyper-phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 which prevents inhibitory association with eIF4E, facilitating eIF4F complex formation. mTORC1 additionally activates p70S6K which indirectly activates eIF4A via repression of PDCD4 and activation of eIF4B. MAPK signaling leads to activation of MNK1/2 (and downstream phosphorylation of eIF4E) via MEK/ERK and p38 pathways, and ERK which with downstream-activated p90RSK, also relieves TSC2 mediated repression of mTORC1. In response to energetic stress AMPK is activated which promotes TSC2 mediated conversion of Rheb-GTP to Rheb-GDP to inhibit mTORC1. Other stress stimuli promote eIF2α phosphorylation that arrests the eIF2 complex in its inactive GDPbound form repressing mRNA translation