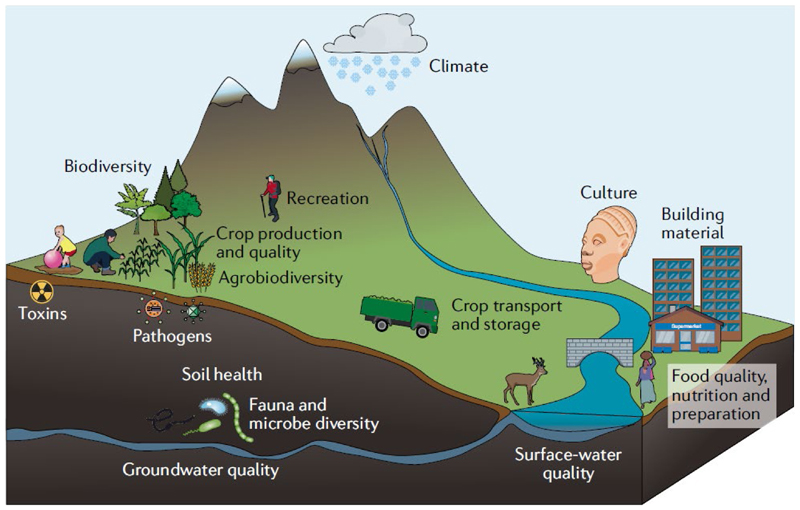
Figure 2. Soil health and global ecosystem services.
Soil health affects human and planetary health through crop production, quality, storage and transportation; food quality and taste; soil contamination, or through climate change, recreation, and culture. Immediacy of soil health effects on plants and soil biota facilitates assessment of causality (for example, soil nutrient availability affects crop production). Cascading effects (such as soil nutrient availability affecting human health indirectly through crop quality and food storage) require causalities to be demonstrated for which in some cases science still needs to be established.