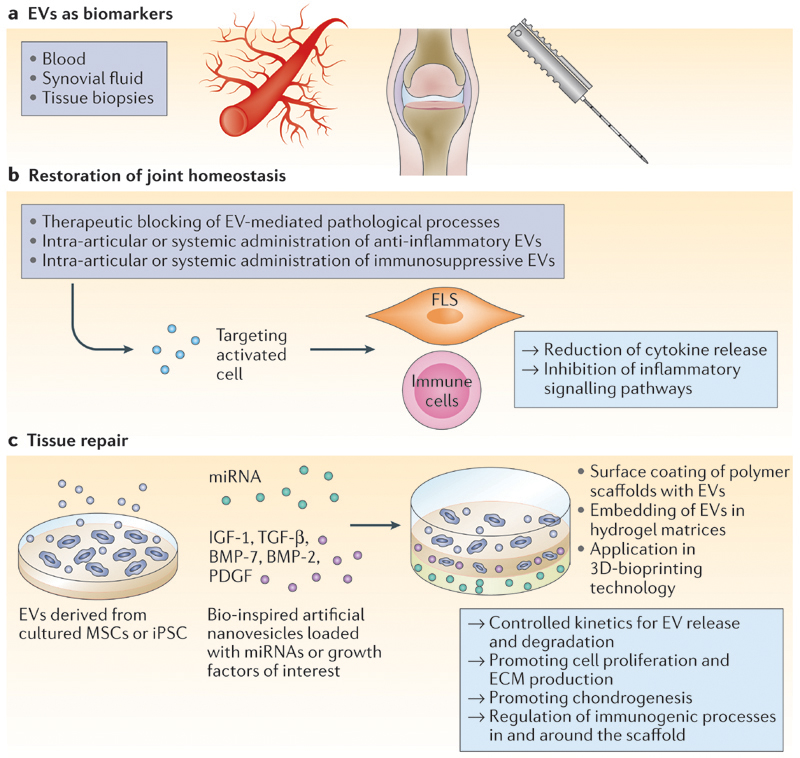
Figure 2. Proposed applications of EVs in joint disease.
a | Extracelluar vesicles(EVs) have bio-marker potential for joint diseases, both to predict disease development in healthy individuals and to monitor disease progression in patients. In the blood, circulating inflammatory EVs can be an alert for early onset of inflammatory joint diseases. In synovial fluid, EVs from patients can provide information about inflammation type, disease state and disease progression. In the context of tissue biopsies, EVs derived from cultured synovial tissue could indicate predisposition for development of autoimmune disease and cartilage disorders. b,c | Regulatory EVs can be exploited for intra-articular injection or for application in biomaterials designed for implantation purposes to restore joint homeostasis and improve tissue repair in patients. BMP, bone morphogenetic protein;|GF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; iPSC, induced pluripotent stem cell; miRNA, microRNA; MSC, mesenchymal stem/stromal cell; PDGF, platelet derived growth factor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β.