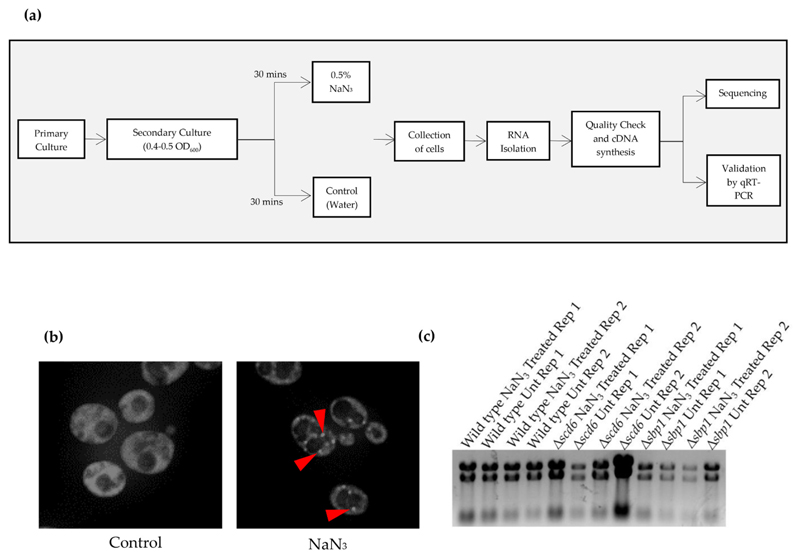
Fig. 1.
(a) Schematic depicting the experimental workflow. Primary yeast cultures were grown for two biological replicates of every strain. For secondary culture, cells were diluted to 0.1 OD600. At mid-log (0.4–0.5 OD600), cells were treated with 0.5% NaN3 for 30 min followed by collection of cells by centrifugation. For control cells, equivalent volume of water was added. RNA was isolated using hot phenol followed by quality check. Sequencing was carried out following cDNA synthesis. Differentially expressed genes were validated by qRT-PCR analysis which was carried out for three technical replicates of each biological replicates; (b) Live cell imaging of cells expressing genomically-tagged PAB1GFP strain treated with NaN3 at the same time as the cells used for isolating the RNA used for RNA-sequencing. Arrows indicate the presence of stress granules; (c) Agarose formamide gel electrophoresis image of the RNA sent for RNA sequencing analysis. Rep 1 and Rep 2 refer to Replicate 1 and Replicate 2, respectively.