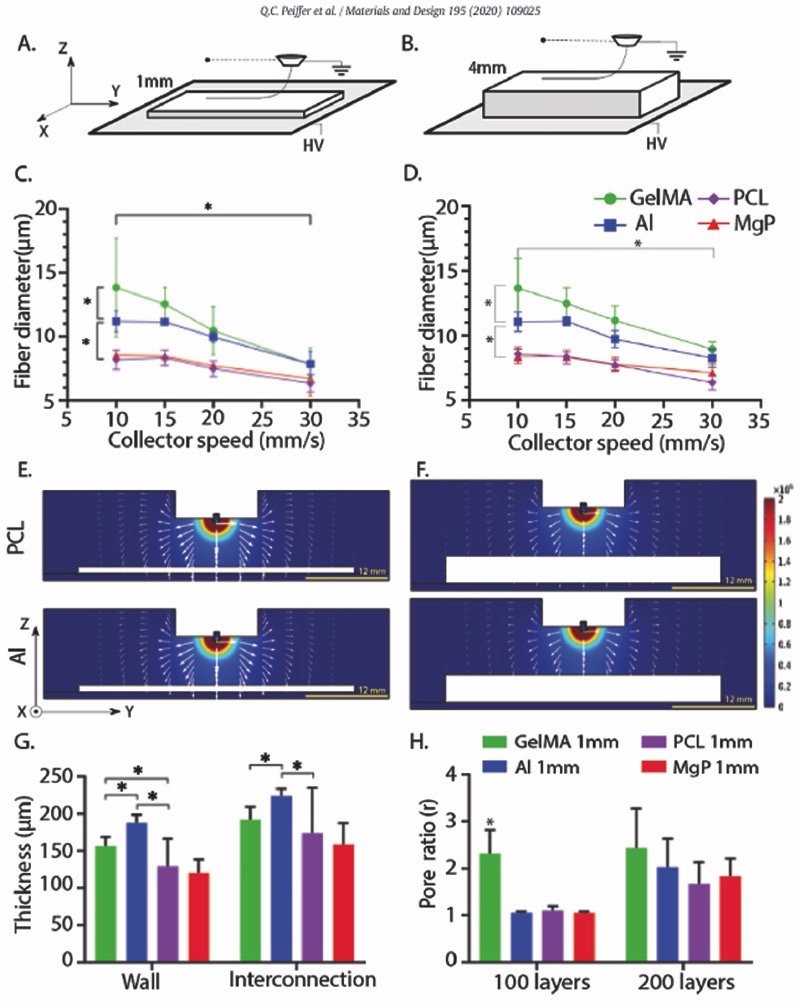
Fig. 2.
Fibre collection on flat-shaped collecting materials (PCL, MgP, gelMA, and Al). A, B) collecting materials of 1 mm and 4 mm high were investigated. C) Effect of collector velocity on fibre diameter of fibres deposited on 1 mm thick collectors. D) Effect of collector velocity on fibre diameter of fibres deposited on 4 mm thick collectors. E) Computational simulation of EF strength (V/m) and distribution (white arrows in logarithmic scale) for non-conductive (PCL) and conductive (Al) collecting material of E) 1 mm and F) 4 mm thick. G) Final scaffold thickness as a reflection of fibre stacking accuracy. Collector velocity = 15 mm/s. H) Pore ratio of scaffolds deposited on 1 mm thick collectors (r = 1 indicates a printed scaffold that conforms to the planned design, while values r ˃ 1 indicates imperfect fibre stacking).* = p ˂ .05.