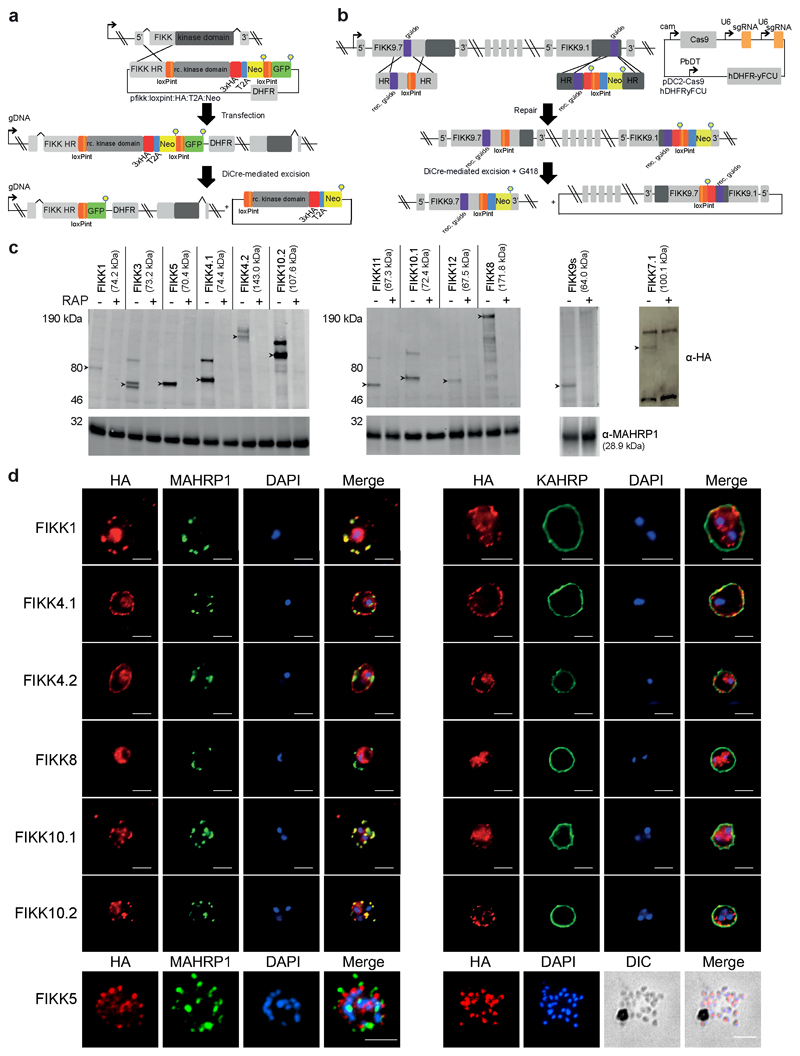
Figure 2. Conditional knockdown strategies for efficient excision and localisation of the FIKKs.
(a) Description of the FIKK cKO strategy using the SLI method (Birnbaum, 2017). Schematic shows the structure of the fikk locus after integration and after Cre-mediated excision. (b) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated introduction of LoxPints into the fikk9.1 and fikk9.7 loci. RAP-treatment induces excision of all FIKKs located on chromosome 9 and expression of the Neomycin resistance cassette. (c) Western blots confirming correct expression and excision of FIKK kinases upon RAP-treatment. MAHRP1 antibody (bottom panel) demonstrates equal loading. FIKK7.1 samples were obtained by HA immunoprecipitation. Arrows – FIKK band at expected size (shown in labels). At least 3 independent western blots were performed for each FIKK with similar results. (d) Subcellular localisation pattern of a selection of FIKK kinases using antibodies against the C-terminal HA-tag fused to each FIKK kinase, MAHRP1 (Maurer’s cleft marker), and KAHRP (knob marker). DAPI was used for nuclear staining. For FIKK5, a late schizont is shown on the left panel, and a burst schizont on the right to demonstrate the localisation of the kinase in merozoites. Scale bar - 5μm. IFAs were performed at least 3 times for each FIKK with similar results.