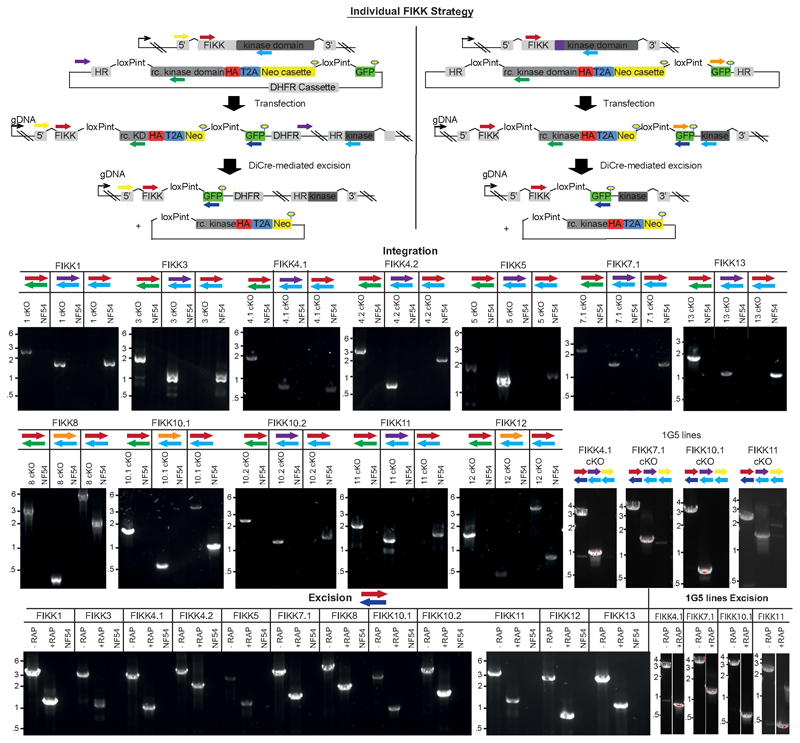
Extended Data Fig. 2. Correct integration of the different FIKK cKO plasmids into the respective endogenous loci and excision of their kinase domains upon RAP treatment.
Schematics describing the different strategies used for generating the conditional FIKK knockout lines using selection linked integration or Cas9. Two LoxP introns were introduced on each side of the recodonised FIKK kinase domain, which was fused to a triple HA tag (red), a T2A skip peptide (blue) and a neomycin-resistance gene, to select for correct integration. Black arrows represent promoters and lollipops depict STOP codons. The relative positions of primers used to confirm correct integration of the plasmids into the respective loci and correct excision of the FIKK kinase domains upon RAP treatment are shown as coloured arrows. HR, homology region; Neo, neomycin-resistance cassette; RAP, rapamycin; rc. KD, recodonised kinase domain. Alongside the schematics are shown the PCR gels confirming correct integration and correct excision. DNA size markers in kbp are indicated on the left. PCRs for each FIKK were repeated at least 3 times with similar results for independent RAP-treatments.