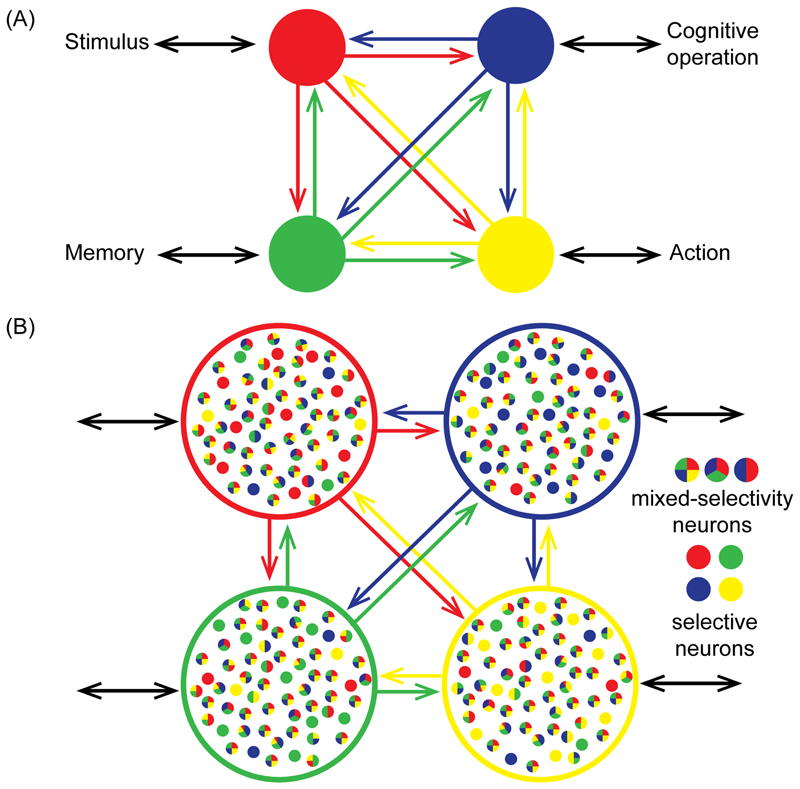
Figure 5. The MD system and cognitive integration.
(A) Depending on its pattern of connectivity, each MD region (colored circles) has direct access to different information and brain operations, here illustrated with just a single link (black bidirectional arrows) for each region. Strong connectivity between MD regions allows assembly of these fragments into the required computational structure. The scheme suggests a basis for partial functional differentiations within a broad context of coactivation. (B) With their varying external connectivity, MD regions may show quantitative differences in neural coding for different task features. Against this background, however, communication between MD regions provides a strong basis for mixed selectivity.