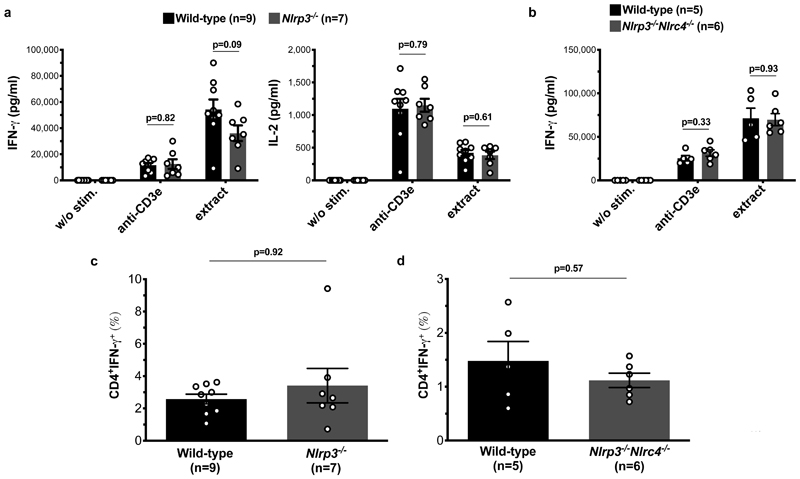
Figure 3. NLRC4 restricts the potency of CD4+ T cell-mediated memory responses against Salmonella in a NLRP3-dependent manner.
The Th1 memory response was assessed by stimulating CD4+ T cells ex vivo with medium only (w/o stim.), anti-mouse CD3e (anti-CD3e), or whole bacterial cell extract (extract). a, CD4+ T cells from wild-type and Nlrp3-/- mice 100 days after challenge with 2.2x104 CFU S. Typhimurium M525P and IFN-γ and IL-2 were measured by ELISA in the cell culture supernatant after 72 and 24 hours, respectively. b, CD4+ T cells from wild-type and Nlrp3-/-Nlrc4-/- mice 90 days after challenge with 1.72x104 CFU S. Typhimurium M525P and IFN-γ was measured as in a. c and d, same experiments as a and b, respectively, the percentage of CD4+ T cells secreting IFN-γ was measured via a cytokine secretion assay. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using two-tailed, unpaired Student's t test assuming equal variances for a and c and two-tailed Mann Whitney test for b and d. All data are representative of two independent experiments.